Synonyms: Worm seeds, Santonica.
Biological source: Artemisia is unexpanded flowering heads of Artemisia brevifolia Wall, Artemisia cina Berg, and A. Maritima Linn and its other species.
Family: Compositae.
Geographical source: It wildly grows in Pakistan, India West Tibet, and Turkey. In India, it is found in Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Kashmir, Kumaon.
Cultivation and Collection of Artemisia
Table of Contents
Artemisia mainly requires sandy loam to loamy soil for cultivation. The soil should not have water logging properties. A well-drained light loam soil rich in organic matter is good for cultivation. It can grow in subtropical areas as a winter crop. It requires cold winter and moderate summer. The cultivation is mainly done by seed propagation. The seedlings are first raised in nursery beds and then transplanted to open fields. The seeds are mixed with sand, spread uniformly over the nursery beds, and covered with a thin layer of soil. The beds are kept moist by a water sprinkler. The seeds germinate within 5 to 8 days. The seedlings are ready for transplantation into land after 6 to 8 weeks. The land should be ploughed and well manured. The seedlings are transplanted at a spacing of 30 to 60 cm between rows and 45 to 60 cm between two plants. Transplanting is mainly done in the evening time. The field should light irrigate after transplantation of seedlings. The crop nutrition is provided by the use of manures and fertilizers. A fertilizer dose of nitrogen, phosphorus pentaoxide, and potassium oxide gives a good yield. Nearly 3 to 4 irrigation is required up to harvesting. The crop is prone to insects so insecticides are used. The crop is ready for harvesting in 4 to 5 months after transplantation. The crop is harvested at the bloom stage to give a good yield. The crop is harvested by cutting the plants 15 to 30 cm above the ground level. The crop is dried and packed for market.
Macroscopical Characters of Artemisia
- Colour: Flowers are yellowish, other parts are whitish-grey.
- Odour: Aromatic, sweet.
- Taste: Bitter, Camphor like.
- Shape: The flower heads are yellow or brown in colour and oval in shape. The flowers are fertile and have tubular corolla, short cylindrical tube, narrow limb and no calyx.
Chemical constituents of Artemisia
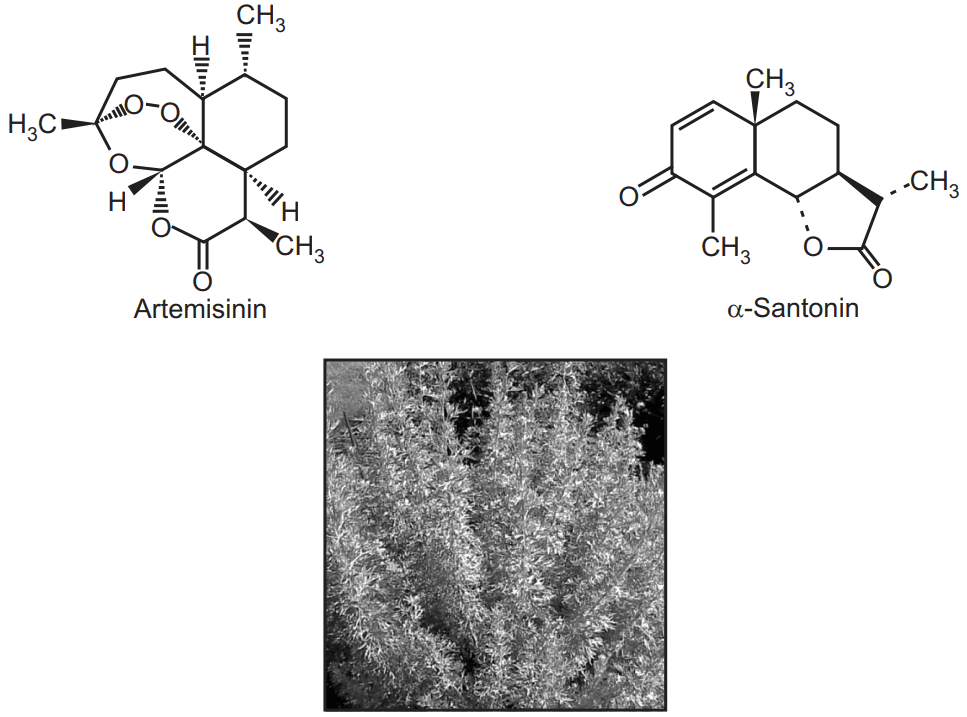
It contains volatile oil (1 to 2 percent) and crystalline substance santonin and artemisin. Other constituents are cineole, pinene, and resin. Santonin is an anhydride of santonic acid that belongs to sesquiterpene lactone. Its amount varies upon the time of collection and type of species.
Chemical Test for Artemisia
Take powdered drug (1gm) and boil it with alcohol (10 ml), filter it. Add sodium hydroxide to the filtrate and warm it until red colour appears.
Uses of Artemisia
It is used as a strong anthelmintic especially for round worms. It has no effect or less effect against hook worm and tape worms.
Substituents: Artemisia vulgaris Linn.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Naphthoquinones
