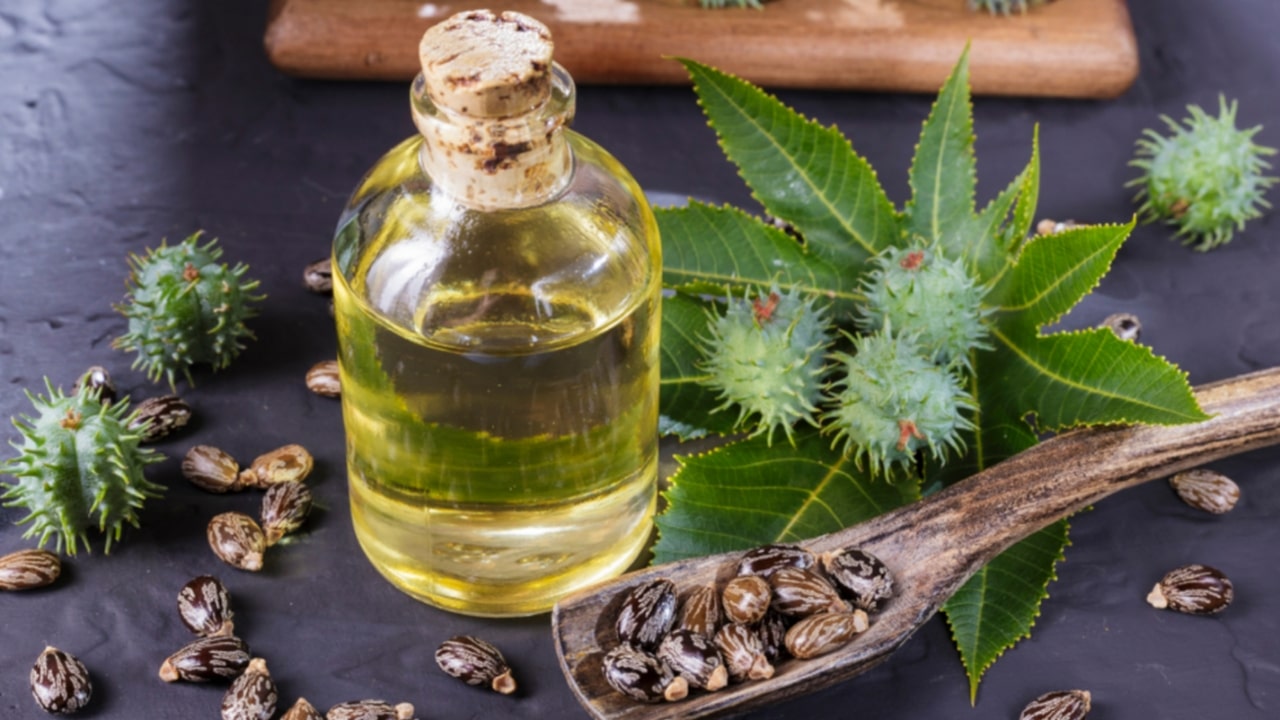
Castor Oil: Castor oil is also known as Ricinus oil.
Biological Source: It is a fixed oil, obtained from the seed of Ricinus communis.
Family: Euphorbiaceous.
Distribution:
The castor bean is considered native to tropical Africa and is grown particularly in arid and semiarid regions. The plant is cultivated in different countries of the world. India, China, Brazil, Ethiopia, Paraguay, Vietnam, and Thailand are the major castor growing countries. In India, the major cultivated zones are Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, and Punjab.
Production of Oil:
Castor beans contain about 30-55% oil. It is extracted by two processes viz. pressing and solvent extraction. The extraction and commercialization of oils from castor seeds is carried out extensively for the oil because there exists a range of free fatty acid contents of the oil due to geographical origin and the method of extraction. Castor oil is extracted from castor beans by cold expression method either by mechanical pressing or solvent extraction or a combination of the two. In mechanical pressing, the seeds are crushed and then adjusted to low moisture content by warming in a steam-jacketed vessel. Then, the crushed seeds are loaded into a hydraulic press (1-2 tonnes) and pressed by mechanical means to extract oil. The extracted oil contains lipase enzymes and some toxic proteins like ricin, which are destroyed by steaming (75-85°C). The resulting oil has a light colour, low free fatty acids, and other impurities. Mechanical pressing recovers only about 45% of oil from the beans and the remainder in the cake can be recovered by solvent extraction.
In the solvent extraction method, the crushed seeds are extracted with any one of the solvents like heptane, hexane, and petroleum ethers in a Soxhlet extractor or commercial extractor, followed by refining. Refining is essential to remove impurities such as colloidal matter, free fatty acid, colouring matter, and other undesirable constituents that make the oil less resistant to deterioration during storage. Before extraction, the castor beans are cleaned by hand, followed by drying in a shed or hot air oven (90°C) to remove moisture. Then the seed coats are separated and finally, seeds are crushed to a required uniform sieve size by mortar and pestle and the sample is placed in the thimble and inserted in the center of the Soxhlet extractor for extraction of oil. After extraction refining castor oil is carried out with degumming, neutralization, de-waxing, deodorization, and bleaching. With this method, the oil recovery is around 50-52% which is higher than the mechanical process. Cold-pressed castor oil has low acid and iodine values, but a slightly higher saponification value compared to solvent extracted oil.
Physical Properties of Oil:
- Type: Fixed oil.
- Colour: Pale yellow to colourless.
- Odour: Soft and faint.
- Taste: Highly unpleasant.
- Solubility: Soluble in alcohol, organic solvents like benzene, chloroform but insoluble in other mineral oils.
Physical Standards:
- Density (Wt/ml): 0.945 – 0.965 g/cm3
- Acid value: Not more than 2
- Flash point: 229.4°C
- Refractive index: 1.473 – 1.477
- Saponification value: 176 – 187
- Iodine value: 81 – 90
- Acetyl value: Not less than 142
- Viscosity: 6.8 poises
- Optical rotation: Between +3.5° and + 6.0°
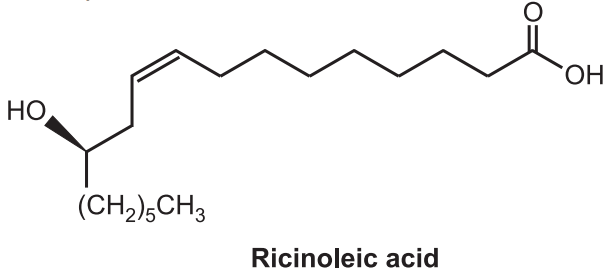
Chemical Constituents: The oil is made up of triglycerides of 91-95% ricinoleic acid, 4-5% linoleic acid, and 1-2% palmitic and stearic acids. The viscosity mainly depends on the presence of ricinoleic acid (95%). Apart from that Oleic acid (6%), Linolenic acid (5%), stearic acid, and palmitic acid are also present.
Chemical Tests:
- Castor oil is miscible with half its volume of light petroleum ether at 55°C.
- An equal proportion of oil and ethanol gives clear liquid even after storage of 3-4 hours; there will be no change in clarity.
Uses:
(a) Industrial Applications: In the textile industry, castor oil is used for moisturizing and removal of grease in fabrics, and the manufacturing of waterproof fabrics. In the steel industry, it is used in cutting oils and lubricants for steel lamination at high temperatures and it is also used in other liquids that are necessary for steelwork. The automotive industry uses castor oil for the production of high-performance motor oil and braking fluids, in the production of fluids for hydraulic devices, artificial leather, varnish, paint, linoleum, insulators, powder, fatty acids, enzymes as a moisturizer for stationary.
(b) Medicinal Uses: Castor oil, seeds, leaves, and roots have numerous medicinal importance. Mainly the oil is used as a laxative. Besides, these are utilized in peritonitis, diarrhea, dysentery, lumbago, constipation, piles, paralysis, sciatica, boils, asthma, dropsy, leprosy, arthritis, amenorrhoea backache, rheumatoid arthritis, anorectal problems, burning feet, period pain, sores, boils, chest, back or abdomen pain, headache, broken tooth, joint pains, pelvis pain, uterine pain, dermatitis, eczema, lactation, nodules in breasts, etc. Ricinoleic acid, the active constituent of the oil, is effective against the growth of various species of viruses, bacteria, yeasts, and molds.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Proteolytic Enzymes
