Cloves are the flower buds of the clove tree, an evergreen also known as Syzygium aromaticum. Found in both whole and ground forms, this versatile spice can be used to season pot roasts, add flavor to hot beverages, and bring spicy warmth to cookies and cakes.
- Synonyms: Clove bud, Laung, Lavang, Caryophyllum.
- Biological source: It consists of dried flower buds of Eugenia caryophyllus (Sprengel) Bullock & Harrison (Syzygium aromaticum Linn).
- Family: Myrtaceae.
- Geographical source: It is native from the Mollucca Island and traditionally cultivated in Tanzania (Zinziber), Madagascar, Indonesia, Srilanka, and India (mainly in Nilgiri hills, Kanyakumari, Kottayam, and Quilon hills of Kerala).
Cultivation and Collection
Table of Contents
The deep rich loamy soil is good for clove cultivation but it can also grow in sandy loam and laterite soil. It favors warm humid climate with annual rainfall in the range of 150 to 250 cm. It grows well at an altitude of 900 meters from sea level. The seeds are sown from August to October for cultivation purposes. The seeds are sown in a nursery bed at a distance of 10 cm. the seeds germinates in four or five weeks and these seedlings are transplanted to pots after six months. These seedlings are kept in pots for nearly about 12 months. Then they are transferred into the open field. The shade is provided in the initial stage because the plants cannot bear the full sunshine. It can also be cultivated along with other plants like areca nut, coconut, or nutmeg. Suitable fertilizers like ammonium sulfate, superphosphate, potash, etc are provided to the plants in two doses. The first dose should be given in May or June and the second dose is in October. The plants started bearing after 7 to 8 years and gives abundant yield per hectare after 15 to 20 years of growth. Generally, the clove plant produces about 3 to 4 kg of drug per year.
The clove buds are handpicked or beating with bamboo. Sometimes platform ladders are also used in the case of tall trees. The collection starts when clove buds change their colour from green to light pink. The cloves are sun-dried and kept free from foreign matter. After drying the colour of cloves changes and becomes crimson or brownish-black.
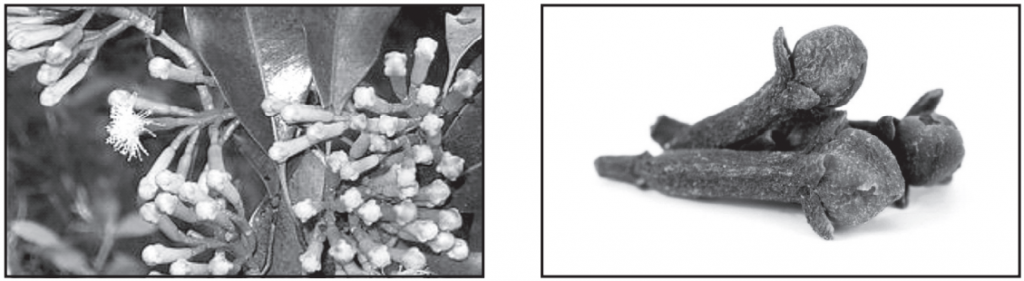
Macroscopic Characters of Clove
- Colour: Crimson red to brown.
- Odour: Characteristic or aromatic.
- Taste: Aromatic and pungent.
- Size: Length (10 to 18 mm), width (3 to 4 mm), and thickness (2 mm).
- Shape: Flower bud is nail-shaped, Hypanthium – Quadrangular (length 10 to 12 mm × diameter 2 to 3 mm), Head – Globulous.
Hypanthium corresponds to the inferior ovary, and a globulous head, surrounded by four divergent sepal lobes consisting of four imbricated petals wrapped numerous incurved stamens. The pulverized drugs show the presence of large secretory cavities, calcium oxalate crystals, pollen grains, fibers with thick, lignified punctate walls.
Chemical Constituents
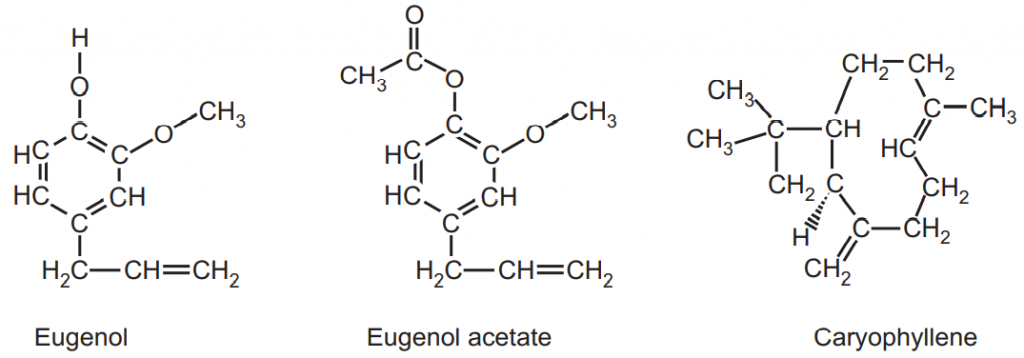
It mainly contains volatile oil (15-20 percent), gallotannins (10 to 15 percent), resin, chromone, and eugenin. Eugenol (70 to 90 percent), eugenol acetate, caryophyllenes, traces of esters, ketones, and alcohols are the constituents of volatile oil that is present in oil ducts of clove.
Properties of Clove Oil
- Colour: Clove oil is colourless to pale yellow.
- Specific gravity: 1.038 to 1.06
- Refractive index: 1.527 to 1.535
- Boiling point: 250°C
It should be stored in proper conditions because it becomes dark and thick on storage.
Chemical Test
Needle-shaped crystals are seen when a section of clove is treated with a strong potassium hydroxide solution.
Uses of Clove
Clove-based phytomedicines are used locally to treat minor wounds after cleansing, as an analgesic (headache, toothache), as an analgesic in disease of mouth, pharynx, or both (in the form of lozenges), in mouthwashes for oral hygiene. Internally it is used to treat symptoms of gastrointestinal disturbances like epigastric bloating, improper digestion, and flatulence.
In Germany, clove-based products are used in mouthwashes for swelling of the mouth and throat. In Indonesia, it is consumed as ‘Kretek’ cigarettes.
Table.1: Adulterants of Cloves
| Sr. No. | Adulterant | Characters |
| 1. | Exhausted cloves | Oil-free or contain very less amount of oil, darker in colour, shrinked, floats on water. |
| 2. | Clove stalks | Generally used for adulteration of powdered cloves, ash value is high, fiber content is high, calcium oxalate prism is present, contains 5 percent of the oil. |
| 3. | Blown cloves | Expanded flowers of the clove tree, stamens free, contain less volatile oil. |
| 4. | Mother clove | Dark brown in colour, oval in shape, slightly aromatic, starchy, contains less volatile oil. |
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Volatile Oils (Terpenoids)
