Concept of Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs): Good Agricultural Practices are specific methods that, when applied to agriculture, produce results that are in harmony with the values of the proponents of those practices.
Objectives:
- Ensuring safety and quality of produce in the food chain.
- Capturing new market advantages by modifying supply chain governance.
- Improving natural resources uses worker’s health and working conditions.
- Creating new market opportunities for farmers and exporters in developing countries.
Cultivation:
It is a scientific approach to the healthy growth of medicinal plants on large scale. Growth is defined as the progressive development of the organs concerning various factors.
Some of the advantages of cultivations are:
- Cultivation ensures the quality and purity of medicinal plants.
- It gives better healthy yield and therapeutic effects.
- It minimizes biodiversity.
- It supplies the raw materials to the industries throughout the year.
- It provides disease-free plants.
- It increases industrialization and helps in the unemployment problem.
General Steps for Cultivation of Plants:
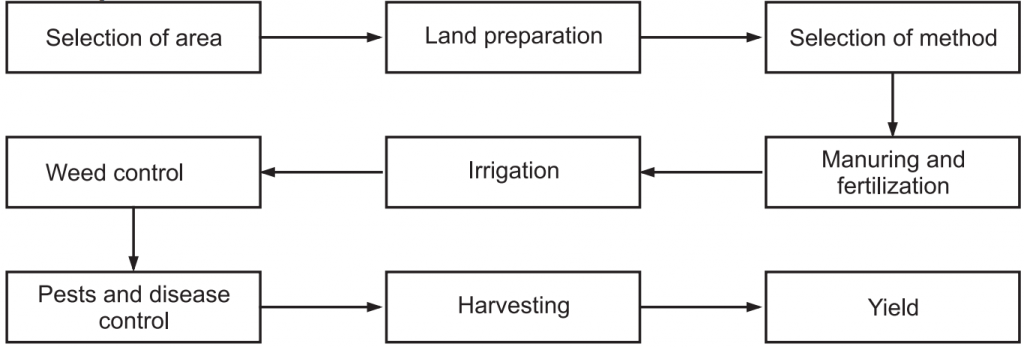
Methods of cultivation:
Generally, two types of cultivation are possible.
(a) Sexual method:
In this method plants are cultivated from the seeds and such plants are called seedlings. This method is also known as seed propagation. Generally, good-quality seeds with a high germination rate should be used for cultivation. Seeds should be free from other seeds and impurities. Examples: Mango, Litchi, Methi, Coriander, papaya, tomato.
Advantages:
- It is an easy method to cultivate plants.
- It gives high yields.
- It gives more number of varieties.
- It is applicable for both monocot and dicot plants.
Disadvantages:
- Sometimes it takes more time to grow.
- The hybrid plant may not get.
- Healthy plants may not get from the same field.
- Asymmetric growth of the plants may occur.

(b) Asexual method:
The vegetative part of the plant, such as steam or root, is placed in such an environment that develops a new plant. Examples: Jasmine, sugarcane, potato, banana, rose.
Advantages:
- It gives a high yield.
- It develops hybrid plants.
- It gives fruits and flowers throughout the year.
- The quality of cultivated plants can improve.
- This method is more useful for monocot plants.
Disadvantages:
- It requires a skilled person.
- Initially, temperature and soil nature have to be controlled.
- This method is time-consuming.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Evaluation of Crude Drugs
