Introduction
Table of Contents
Steroidal hormones produced in the adrenal cortex mainly it is involved in the regulation of physiological activity, such as:
- Immune response
- Carbohydrate metabolism
- Regulation of inflammation
- Protein metabolism
- Regulation of blood electrolyte level.
Types of Corticosteroids:
1. Glucocorticoid
2. Mineralocorticoid
1. Glucocorticoid
- Dexamethasone
- Prednisolone
- Fludrocortisone
Function
- Glucocorticoids are used in the treatment of joint pain and inflammation, dermatitis, allergic reaction, asthma, Hepatitis, ulcerative colitis.
- Used in the treatment of Addison’s disease.
- Topical formulations are used for skin infection, asthma, and laryngitis.
Side Effects:
- Anxiety, depression, psychosis.
- Hyperglycemia.
- Osteoporosis.
- Retinopathy.
Biosynthesis
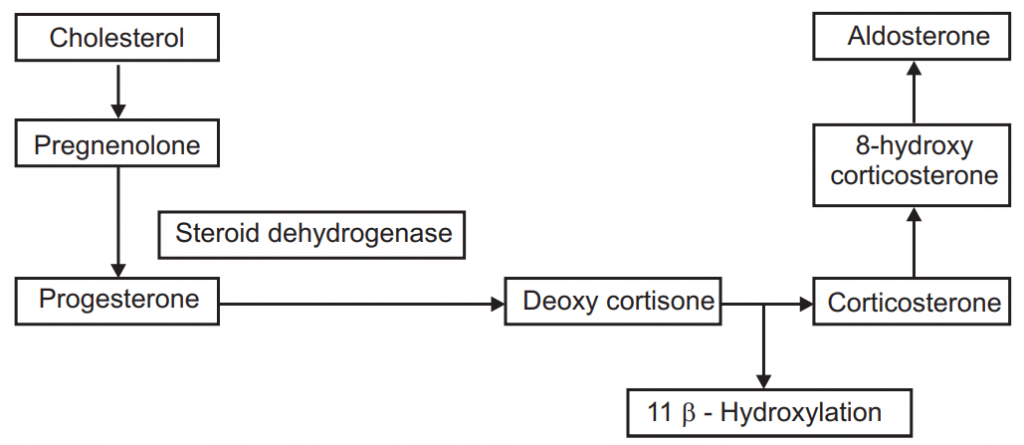
Pharmacological Action:
Carbohydrate and Protein Metabolism:
- It promotes glycogen deposition in the liver.
- It promote gluconeogenesis.
- Induce protein break down.
- Increases uric acid excretion.
Fat Metabolism:
- Glucocorticoids induce lipolysis due to glucagon, growth hormone, adrenaline, and thyroxine.
- Break down of triglyceride enhanced by cAMP.
- Loses fat deposited over face, neck, and shoulder producing ‘moon face’, ‘fish mouth’ and ‘buffalo hump’.
Calcium Metabolism:
- It enhances the renal excretion of calcium.
- Results loss of Ca++ from bone, leading to negative calcium balance.
Cardiovascular System:
- Maintain myocardial contractility.
- It producing minor hypertension.
Skeletal Muscle:
- Enhances muscular activity.
- Excess glucocorticoid action leads to muscle wasting and myopathy.
CNS:
- Produces euphoria, insomnia, anxiety
Stomach:
- It increases gastric acid and pepsin secretion.
Blood and Lymphoid Tissue:
- Destruction of lymphoid tissue.
- Increasing the no. of RBC by inhibiting hemolysis.
- Decrease the no. of circulating lymphocytes, monocytes, basophils, eosinophils.
Effect on Immune Response:
- Blocks the synthesis of cytokines.
- Block the action of cytokines.
- Increasing the expression of a gene coding for an enzyme that degrades inflammatory mediators.
Hydrocortisone (Cortisol):
- Mainly used for the treatment of ulcerative colitis and hormone replacement therapy.
Prednisolone:
- It is 4 times more potent than hydrocortisone and more selective. Act as anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, and used for the treatment of autoimmune disease.
Dexamethasone:
- Potent and selective glucocorticoid. It is used for the allergic and inflammatory condition, which is long-acting.
2. Mineralocorticoid
- Aldosterone is the prototype that produces mineralocorticoid effects.
- By acting on the distal tubule aldosterone enhances the absorption of Na+.
- A similar effect occurs in the colon, sweat gland, and salivary gland.
- Deficiency of mineralocorticoid action leads to hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, acidosis.
- Hyperaldosterinism results in positive Na+ balance increased plasma Na, hypokalaemia, alkalosis.
ACTH Inhibitors:
- Aminoglutethimide: Which stop/inhibit the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone. Used in the treatment of adrenocortical cancer.
- Metyrapone: 11 beta-hydroxylase enzyme inhibitor – used in Cushing’s syndrome and test of pituitary efficiency.
- Mifepristone: Progesterone antagonist.
- Ketoconazole: Inhibit the synthesis of all hormones in the testes and adrenal cortex, used in the treatment of Cushing’s syndrome and hirsutism in females.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Diabetes Mellitus