Overview of Cruciferae
Habit:
- These are annual herbs.
Leaves:
- The leaves are radical and cauline, simple, alternate, often lobed, or rarely pinnately compound.
Inflorescence:
- A raceme (corymbose towards the top).
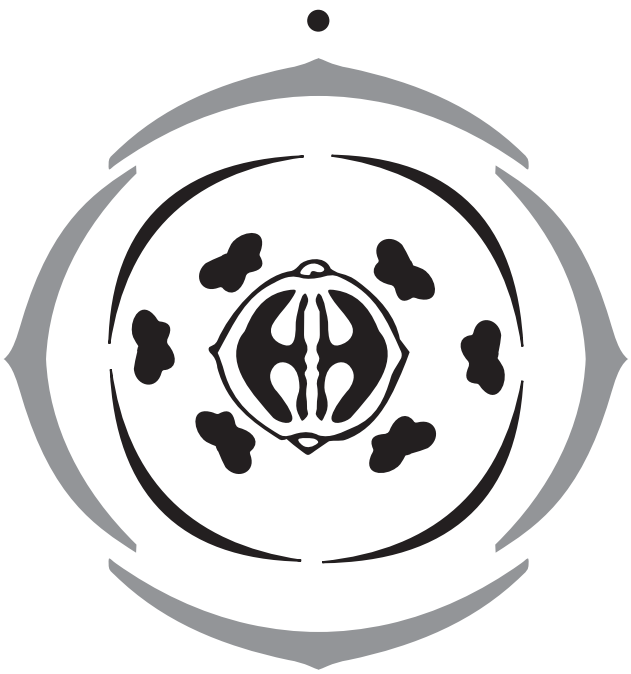
Flowers:
- The flowers are regular and cruciform, bisexual, and completely hypogynous.
Calyx:
- They are sepals, 2+2, which are free, and in two whorls.
Corolla:
- There are four petals, free, in one whorl. They alternate with the sepals. They are cruciform. Each petal has a distinct limb and claw.
Androecium:
- There are six stamens in two whorls, two short, outer ones and four long, inner ones (tetradynamous).
Gynoecium:
- There are two syncarpous carpels. The ovary is superior, at first one-celled, but later two-celled owing to the development of a false septum. There are often many ovules in each cell, sometimes only two. They are anatropous or campylotropous. The placentation is parietal.
Fruit:
- The fruit is a long, narrow siliqua or a short, broad silicula.
Seeds:
- These are exalbuminous. The embryo is curved. The seeds remain attached to a wiry framework, called the replum, which surrounds the fruit.
Floral formula:
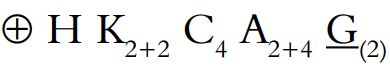
Examples: Black mustard (Brassica nigra).
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Characteristics of Compositae
