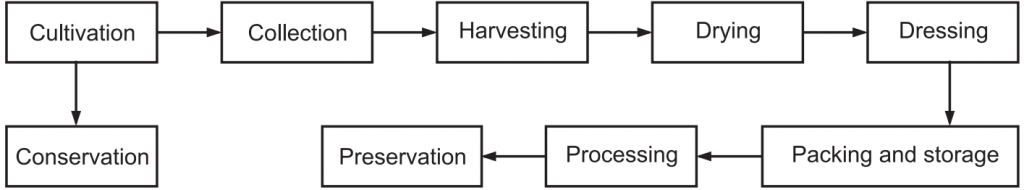
Cultivation and Collection of Drugs of Natural Origin: Medicinal plants have curative properties due to the presence of various complex chemical substances of different compositions, which are found as secondary plant metabolites in one or more parts of these plants. These plant metabolites, according to their composition, are grouped as alkaloids, glycosides, corticosteroids, essential oils, etc.

World Health Organization (WHO) has estimated that at least 85% of the world population relies on traditional systems of medicine for their primary health needs. These systems are largely plant-based. According to WHO, over 21000 plant species are useful in the preparation of medicines. Due to the growing awareness about side effects and complications of chemical and synthetic medicines, cosmetics, and health supplements, the usage of herbal products has gained importance both in the Eastern and Western Worlds.
It is estimated that more than 70,000 plant species, from lichens to towering trees, have been used at one time or another for medicinal purposes. The herbs provide the starting material for the isolation or synthesis of conventional drugs. India is endowed with a rich wealth of medicinal plants, which ranked our country in the list of top producers of herbal medicines. The varied agro-climate conditions in India make this suitable for growing a wide range and variety of valuable medicinal plants. This production of medicinal plants generates increased employment opportunities for the farmers and enhances their incomes. But due to overpopulation and other conditions, the total forest area is reducing, which has reduced the total cultivation/ collection of medicinal plants in India. We may lose the wealth of medicinal plants if this deforestation continues, which will affect the growth of our economy.
Therefore, it is essential to cultivate at a large scale and to conserve the heritage of medicinal plants. Recently Indian Government has set up a national-level body, the NMPB (National Medicinal Plant Board) for the growth and development of medicinal plant sectors in the country.
General guidelines on good agricultural practices (GAP) for medicinal plants are required to distribute to all the growing sectors, which describes general principles and provides technical details for the cultivation of medicinal plants, their quality control measures, where applicable. We are still at the developing stage of the cultivation of medicinal plants because there is no standard operating procedure for cultivation in India. Indian farmers are facing various problems in the cultivation of medicinal plants because of lack of proper agro-technology, high fees for packages developed by various organizations, lack of reliable and standardized technology package, lack of planting material, market potential and system, cultivated wild plants, organic farming techniques, etc. Knowledge of post-harvest processing technology of plants for the extraction of chemicals and preparations of the active formulation is still needed.
Various aspects of medicinal plant cultivation include old philosophies, the modern impact of traditional medicines and methods of assessing the spontaneous flora for industrial utilization, climatic variations, biological assessment, formulation, process technologies, phytochemical research, and information sources. Indian herbal Industry is at the blooming stage, but the supply of raw materials through the cultivation of medicinal plants is very difficult in all seasons. In India, various medicinal plants are cultivated and domesticated, therefore, International trade is looking to procure medicinal plant materials from India for the production of pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmeceutical preparations.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Adulteration of Drugs of Natural Origin
