Aim: To determine the pulse rate.
Requirement: Stopwatch.
Theory: The pulse is the pressure wave created by the alternate constriction and dilatation of arteries after each systole of the heart. The pulse may be felt at any artery near the body surface that can be compressed against a bone e.g. common carotid artery and radial artery. The number of pulses recorded per minute is called pulse rate. The normal pulse rate is the same as the heart rate, about 70-80 beats/minute. Pulse is examined to diagnose the conditions of the heart, arteries, or blood pressure.
A pulse rate above normal is called Tachycardia and a decrease in pulse rate than normal is called Bradycardia.
Procedure:
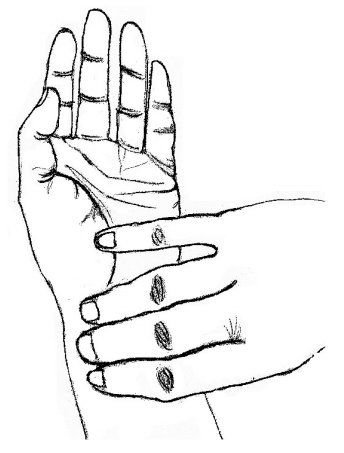
- Locate the radial artery at your own wrist level.
- Palpate the radial artery by pressing them with a finger against the underlying bones (the pulse will be felt).
- Record the pulse for 1 minute.
- Take three readings at the interval of 5 minutes and calculate the mean pulse rate.
Note: Normal Values of pulse rate/minutes:
- Neonates: 140 beats.
- Children: 100 beats.
- Adults: 60-80 beats.
Observation table:
| Sr. No. | Observation No | Pulse rate (pulse/min) |
| 1. | 1st reading | |
| 2. | 2nd reading | |
| 3. | 3rd reading | |
| 4. | Mean |
Result: The pulse rate was found to be ”x“ pulses per minute.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Reticulocyte Count of Own Blood
