Organization of Drug Store
Drug store management is one of the important aspects of the pharmaceutical business. It is also called a retail pharmacy, which consists of final activity and is a place where drugs will be in the hands of the patients/consumers or to provide services to the patients/consumers. The word retail is derived from the French word Retailer, meaning to cut a piece off or to break-bulk. For successful of any retail firm, some important factors are taken into consideration. As pharmacy is a specialized field, some of the factors are different compared to other retail outlets. Ideal drug store requirements are mentioned below:
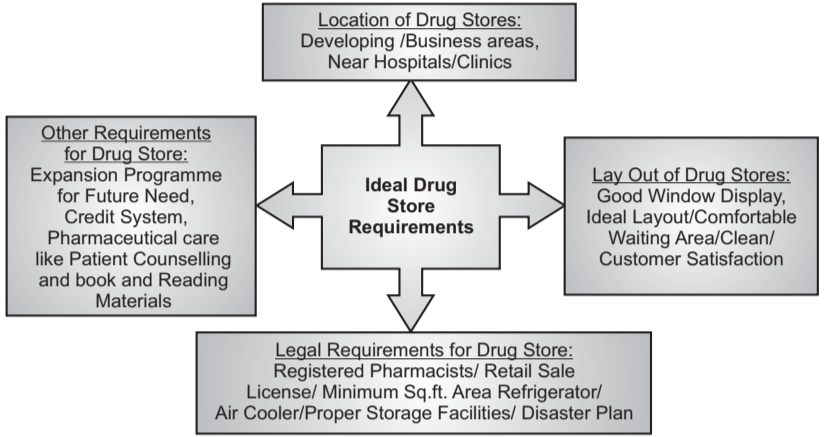
Purchasing of Materials:
Purchasing or procurement is an important aspect of material management in the pharmaceutical field. Purchasing any materials/equipments related to pharmacy should be a genuine activity. A well-planned and sound purchasing policy ensures sufficient purchases to meet all anticipated needs but avoids either over stocking or under stocking. Economical, efficient, and timely purchases should be an objective of a sound purchasing policy.
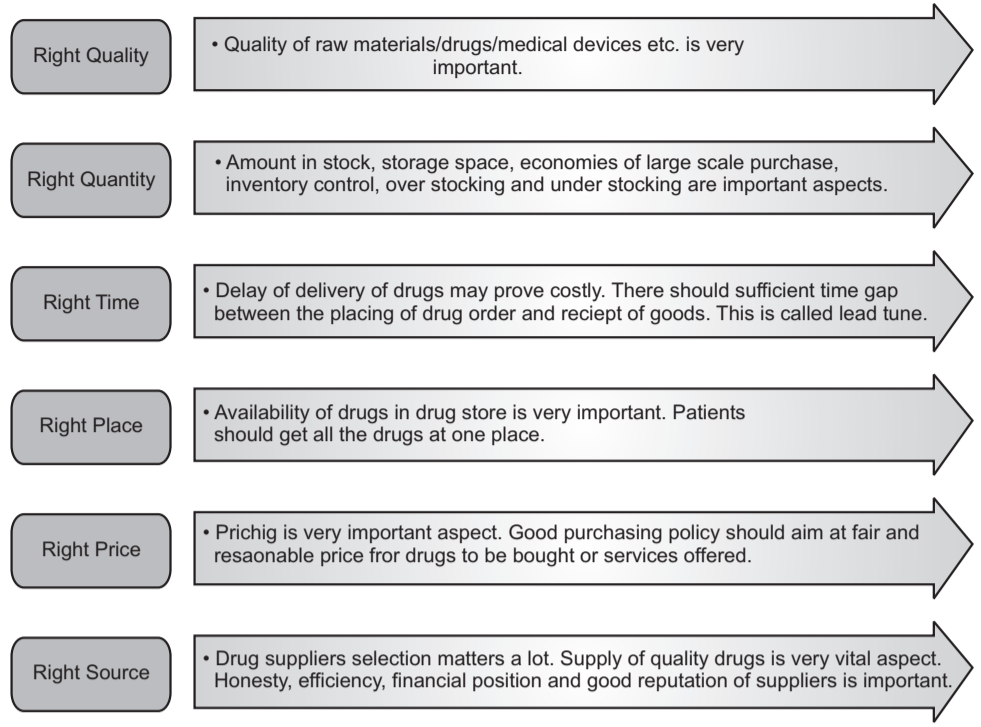
Purchasing Procedure:
Once the selection of suppliers is done, then purchasing of drugs is done based on drug store requirements. Orders can be placed from a single supplier or multiple suppliers. For continuity of supply of drugs most reputed, trusted suppliers need to be selected. The mode of payment for purchase depends on the supplier and buyer. It may be through credit, online, or cash transactions.
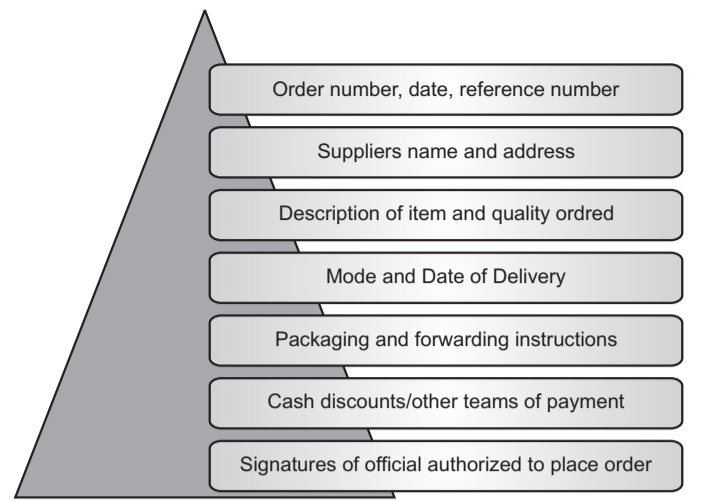
Purchase Order:
An order may be defined as an offer to buy a specific drug product from suppliers. The order should be clear and free from any errors. It is one of the important written documents for future references. The particulars mentioned in purchase orders are:
Types of Materials Stocked and Storage Conditions
Drug stores are used to store all kinds of products/materials like; capsules, tablets, liquid dosage forms, injections, antibiotics, narcotics, and psychotropic substances, biologicals, medical devices, etc.
Storage/Store keeping is directly concerned with the physical storage of goods. Proper storage offers protection against fire, damage, deterioration, theft, losses, etc. It helps in identifying and locating drugs through indexing, labels, and identification marks. Another important aspect of storage is; it helps in effective inventory control. Storage conditions of pharmaceuticals should possess the following:
- Adequate temperature.
- Sufficient lighting.
- Clean conditions.
- Humidity control.
- Cold storage facilities.
- Adequate shelving to ensure the integrity of the stored drugs.
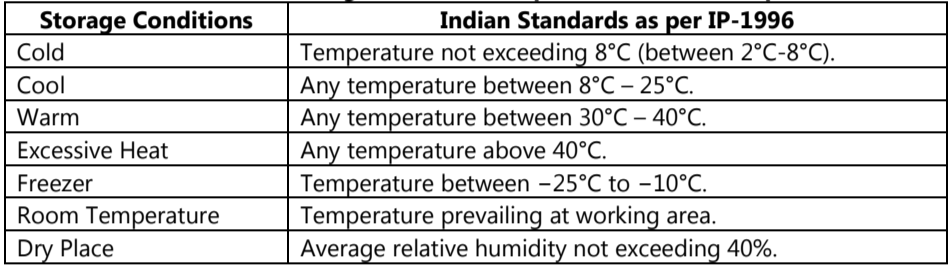
Storage Conditions as per Indian Pharmacopoeia:
Table.1: Storage Conditions as per Indian Pharmacopoeia
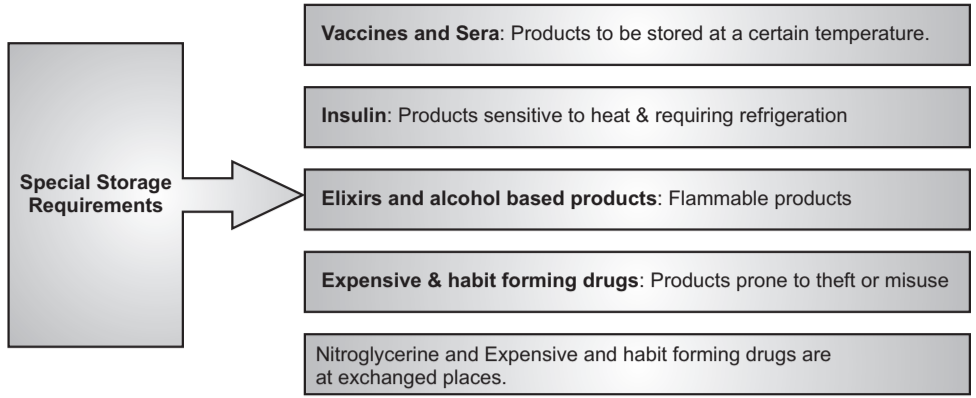
Inventories in Drug Store:
Inventory means stock. To stay ahead in the market, drug stores need to take into consideration demand and supply. Buying the right quantity is important to the success of the business in several ways. Inventory is required to satisfy future demands and plans of the drug store. One of the most important aspects of inventory is to have the items in stock at the moment they are needed. Inventory is the availability of goods or materials at any given time. The inventory system controls and monitors levels of inventory and regulates what levels should be maintained when stock should be refilled, and how large orders should be placed. Inventories are affected by fluctuations in demand and manufacturing lead times which are covered by reserve stock or safety stock. Inventory is in the form of money and asset for an organization. The purchase and holding of a minimum supply of items will give a better return on investment and inventory turnover. Many active ingredients like antibiotics and vitamins deteriorate very fast if they are not properly stored. Hence, these materials should be produced as and when required. A well-managed inventory can help in cost reduction of the organization. Thus, the savings can be invested by the organization for other profitable ventures. The various types of materials which are kept as inventories are all types of drugs, over the counter drugs, and medical devices as per schedules mentioned in the Drugs and Cosmetic Act, 1945.
Purpose of Inventory Management:
The main objectives of Inventory management are:
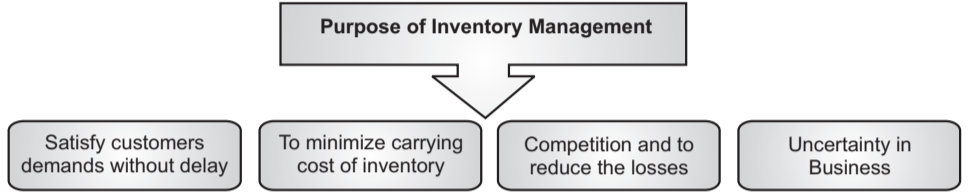
1. Satisfy customer’s demands without delay: The main objective of inventory management is to satisfy customers’ demands by supplying drugs/medicines without endless delay.
2. To minimize the carrying cost of inventory: Another important objective of inventory management is to reduce investment in inventory at a minimum level to maximize productivity.
3. Competition: To stay ahead in a competitive market, drug store needs to dispense drugs as per requirement in the market.
4. To reduce the losses: There may be an unexpected loss of goods due to theft, obsolescence, and wastage, etc.
5. Uncertainty in Business: In a rapidly changing environment, the market (business) is facing multiple challenges in all means. To standardize the market, drug store has to go for inventory management.
Advantages of Inventory Management:
The aim of inventory management should be the timely delivery of goods and services.
- By maintaining the inventory there will not be a stoppage of dispensing of drugs.
- Helps in minimizing loss due to deterioration, obsolescence damage, and pilferage.
- The economy in purchasing.
- Eradicates the possibility of similar ordering.
Disadvantages of Inventory Management:
There are certain disadvantages of inventory management like:
- It becomes difficult and costly in the case of large orders of drugs.
- It requires skilled and trained personnel.
- Market and seasonal fluctuations may create a loss in business.
Techniques of Inventory Management:
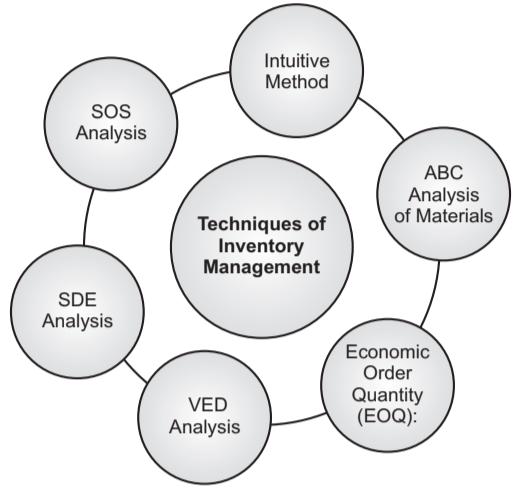
Intuitive Method: The in-built method is aided by the well-known want book. This is the most common method in practice today and surely the least effective. Items are recorded in the want book when the number of units in stock reaches one to three, and the amount ordered is the best estimate of the person in charge of inventory.
ABC Analysis of Materials: It enables the management to plan efforts to get. It is a powerful approach in the direction of cost reduction, as it helps to control items required for production with a selective approach. Proper color codification may be adopted for ABC categories of items.ABC analysis is called always better control.
Table.2: ABC Analysis
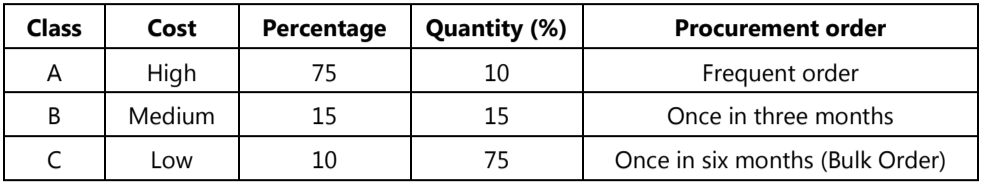
What are Class ABC Items?
Class A: These are fundamental items. They are bulk drugs that are costly. The cost of procurement of these items is high. In terms of quantity, they are only 10%. Class A items are antibiotics and costly drugs. Searching for many sources of suppliers for class A items will be more economical. As the Class A items are very costly accurate forecast is needed for these items.
Class B: These are not so costly items as compared to Class A items. Class B items constitute 15% in terms of quantity. They are usually excipients used for drugs. These are not fundamental items compared to Class A items.
Class C: These are also not fundamental items. These are economical items. They are excipients used for drugs. Class C items constitute 75% in terms of quantity. The procurement order is made once in Six months. ABC analysis helps in reducing clerical costs and rationalizes the number of orders and reduces overall inventory.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
The EOQ is one of the important methods of inventory management. In the pharmaceutical industry, high cost is invested on materials with longer procurement time. EOQ is represented is by the formula:
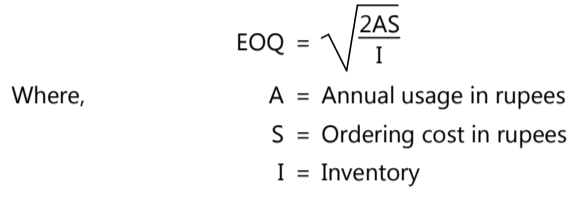
EOQ is based on the inter-relationship of costs which shows carrying costs. As order quantities go up, so do carrying costs, but ordering costs go down. Conversely, as order quantities go down, so do carrying costs, but carrying costs go up. EOQ analysis determines whether these costs are in balance. The EOQ equation shows that the most economic lot size is the function of the square root of the annual usage of items expressed in rupees. A material manager should decide how much to buy and when exactly to buy. Excess inventory will increase the chances of obsolescence. Purchasing of materials should be done at right time, using efficient forecasting methods carefully. Ordering to the nearest trade quantity or quality may be essential, as low demand and supply will be uneconomic to produce and quote. The order quantity could be altered to get certain benefits of transportation and discounts offered for bulk purchase of materials. In the case of perishable goods, the quantity has to be adjusted to the shelf life of the item. When prices fluctuate, a dynamic programming technique has to be used to determine the quantity of purchase.
VED Analysis:
VED is one of the important types of inventory management. VED analysis is done to control critical inventory situations. VED analysis is called Vital Essential Desirable.
V-Vital: Item without which production will completely stop.
E-Essential: These items are also called alternative items.
Desirable: These items can be endured for a long period.
SDE Analysis:
SDE analysis is based on spares availability of an item:
S-Scarce items: These items are specially imported and those which are very much in short supply. Due to the scarcity of these items, they are procured at yearly intervals.
D-Difficult items: These are difficult for availability.
E-Easy items: These items are easily available. They are produced locally. Due to their easy availability, firms may not require to hold these items in large volumes in their stock.
SOS Analysis:
SOS Analysis is done, keeping in view the seasonality or non-seasonality of the item.
- S – Seasonal Items
- OS – Non-seasonal Items
Depending on the seasonality and non-seasonality of the items, procurement actions vary. Example: Sales of certain commodities, such as; cough and cold products, increase between rainy and winter season due to the cold and flu season whose procurement is seasonal, these companies need to procure their requirement for a longer duration to adjust their production plans. Non-seasonal items are available throughout the year without any major price variation. Since seasonal items, which are available for a limited period, are procured in bulk to manage the production process throughout the year.
Recent Trend in Inventory Management:
Use of computers in inventory control. As computerization of inventory control will provide effective control and increase profitability. Computerization has reformed inventory management with the help of technology company can trace their goods till it reaches the hands of a customer. Reports which can be generated by computer like:
- Forecasting: Reports can be generated for sales history, sales forecast, and forecasting techniques.
- Material planning reports can be maintained for material requirements and bills of material.
- Inventory management: Reports regarding Maximum inventory level, Minimum inventory level, and ABC analysis can be maintained.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Clinical Pharmacy
