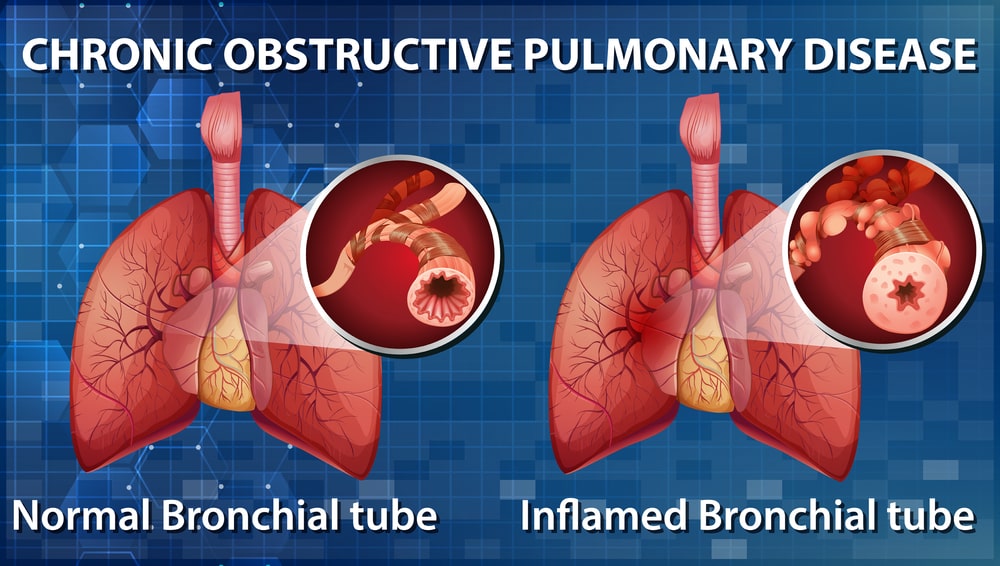
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic disease of the lungs that damage the airways as well as the lungs resulting in difficulty to breathe. COPD may have obstructive bronchiolitis, emphysema, or a combination of both conditions. While there is no cure for COPD, following drug therapy may help patients with COPD to improve their quality of life.
1. Bronchodilators: Bronchodilators help to relax the muscles of airways to ease breathing. The following drugs are acting as bronchodilators
- Inhaled β2-agonists are either short-acting (4-6 h) like albuterol, levalbuterol, pirbuterol, salbutamol, and terbutaline or long-lasting (12-24 h) like β2-agonists are salmeterol, formoterol, indacaterol, or vilanterol. β2-agonists are generally safe but may cause fast heartbeat, tremors, and cramping of the hands, legs, and feet.
- Anticholinergics are also inhaled medications with slower onset of action as compared to β2-agonists. Short-acting anticholinergic (Ipratropium) have an onset of approximately 15 minutes and lasts for 6-8 h whereas long-acting start effects in 20 minutes and may last for 12 h (aclidinium) or 24 h (tiotropium, umeclidinium). The most common side effects are dry mouth and difficulty passing urine resulting in urinary retention.
- Theophylline is a bronchodilator that is not commonly used for COPD as most patient prefers inhaled bronchodilators, it is usually administered orally. A common side effect is a shakiness, but very serious side effects are severe nausea, vomiting, heartbeat irregularities, and seizures. So the blood concentration of theophylline is usually monitored in the patients.
2. Steroids: Steroids or corticosteroids are medications used to reduce inflammation in the airways. They are usually administered by inhalation in combination with other bronchodilators. It takes a week or more for the beneficial effects of steroids to when inhaled, so it may be given by oral route which acts faster (within 24 h). Side effects of steroids depend on the dose, duration of administration, and route of administration. The most common side effects of steroids are sore throat, hoarse voice, and infections in the throat and mouth. Steroids given by oral route regardless of dose for a long time may cause bruising of the skin, weight gain, weakening of the skin, osteoporosis, cataracts, high blood pressure, increased blood sugar, mood changes, muscle weakness, swelling of the ankles or feet.
3. Other Medications: In patients with frequent COPD exacerbations, roflumilast and long-term use of azithromycin was found to be beneficial. Both these drugs are given orally and have been shown to decrease the number of exacerbations. Mucolytics may be added to thin mucus (phlegm or sputum) for easy cough. Some patients need oxygen to treat low oxygen levels.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Symptoms of Respiratory Disease