Aim: To determine the effect of osmotic pressure on red blood cells (RBCs) of own blood sample.
Requirements: Disposable needle (26G), dropper, microscope, 70% alcohol or any other suitable marketed antiseptic, glass slide and coverslip, isotonic (0.9% NaCl), hypertonic, hypotonic solution.
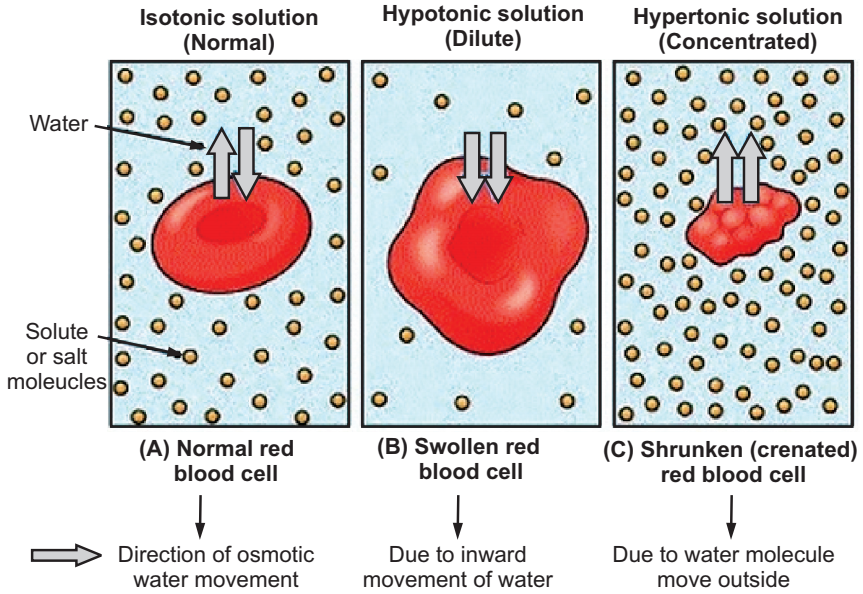
Principle: The cell membrane of RBC acts as a selectively permeable membrane that carries out the process of osmosis i.e. movement of solvent or water from dilute to the concentrated solution. The effect of osmotic pressure can be observed by creating hypotonic and hypertonic conditions. The osmotic fragility of RBCs is vital to determining their functional status. When RBCs are placed in a hypotonic solution, water enters the cell through the selective membrane and swells till hemolysis occurs (rupturing of RBCs). On the other hand, RBCs in hypertonic solution undergo shrinkage due to the loss of water molecules through the selective membrane and resulting in crenation (notched projections on the surface).
Procedure:
- Take four clean glass slides and mark them as A, B, and C.
- Add a drop of hypertonic solution, hypotonic solution, and isotonic solution on the glass slides A, B, and C respectively.
- Sterilize the tip of the ring finger with a suitable antiseptic solution.
- Gently, prick the fingertip with a pricking needle to obtain a few drops of blood on slides A, B, and C.
- Mix the blood immediately with the respective solution.
- Place a coverslip on each glass slide and keep these slides undisturbed for 10 minutes.
- Observe the size and shape of RBCs for each slide under the microscope and note the changes.
Note: The size of RBCs in isotonic solution shall be considered as the standard and changes in the size and shape of RBCs in other solutions will be compared accordingly.
Observation:
| Slide | Type of solution used | Size and shape of the cell | Inference |
| A | Hypertonic solution | ||
| B | Hypotonic solution | ||
| C | Isotonic solution |
Result: The RBCs were found to swell in a hypotonic solution, to shrink in a hypertonic solution and there was no change in size and shape of RBCs in an isotonic solution. The effects of various solutions on RBC were observed.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : White Blood Corpuscles Count