Endogenous Antioxidants: The body having several endogenous defense mechanisms systems that reply and self-protect against free radical-induced cell damage. The name of endogenous antioxidants enzymes are glutathione peroxidase, catalase, and superoxide mutase (SOD)-metabolize. The oxidative toxic intermediates neutralize by using several micronutrient cofactors such as selenium, iron, copper, zinc, and manganese for optimum catalytic activity. Various researchers have been suggested that an insufficient dietary intake of these trace minerals may cooperate with the efficacy of these antioxidant defense mechanisms. The various research articles represented that consumption and absorption of these significant trace minerals may reduce with aging. Intensive agricultural methods have also resulted in an important reduction of these precious trace minerals in our soils and the foods grown in them. Glutathione is a significant water-soluble antioxidant. It is synthesized by using amino acids glycine, glutamate, and cysteine. Glutathione directly quenches ROS such as lipid peroxides. In addition, it also plays a chief role in xenobiotic metabolism Exposure of the liver to xenobiotic substances increases oxidative reactions through the up-regulation of detoxification enzymes that is cytochrome P-450 mixed-function oxidase. When an entity is exposed to elevated levels of xenobiotics, more glutathione is utilized for conjugation (a key step in the body’s detoxification process) making it less existing to serve as an antioxidant. Many researchers have been suggested that glutathione and vitamin C work interactively to quench free radicals and that they have a sparing effect upon each other.
Lipoic acid, yet another significant endogenous antioxidant, and is categorized as a “thiol” or “bioethanol. It is a sulfur-containing molecule that is recognized for its involvement in the reaction that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of alpha-keto acids, such as pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate, in the Krebs cycle. Lipoic acid and its reduced form is dihydrolipoic acid (DHLA). That is able of quenching free radicals in both lipid and aqueous domains and as such has been known as “universal antioxidant. The lipoic acid may also use its antioxidant effect by chelating with pro-oxidant metals. Many researchers have been suggested that lipoic acid has a sparing effect on other antioxidants. Supplemental lipoic acid is to protect against the symptoms of vitamin E or vitamin C deficiency,
Some Endogenous Antioxidants are given here:
- Bilirubin
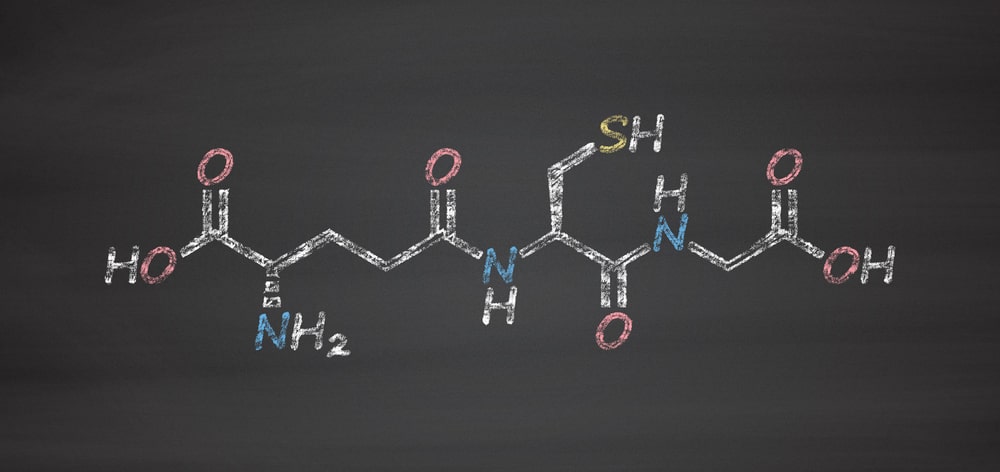
- Thiols, e.g., glutathione, lipoic acid, N-acetyl cysteine
- NADPH and NADH
- Ubiquinone (coenzyme Q10)
- Uric acid
Enzymes as an antioxidant:
- copper/zinc and manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase (SOD)
- Iron-dependent catalase
- Selenium-dependent glutathione peroxidase.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Functional Foods For Chronic Disease Prevention