FIBRINOLYTIC SYSTEM
Table of Contents
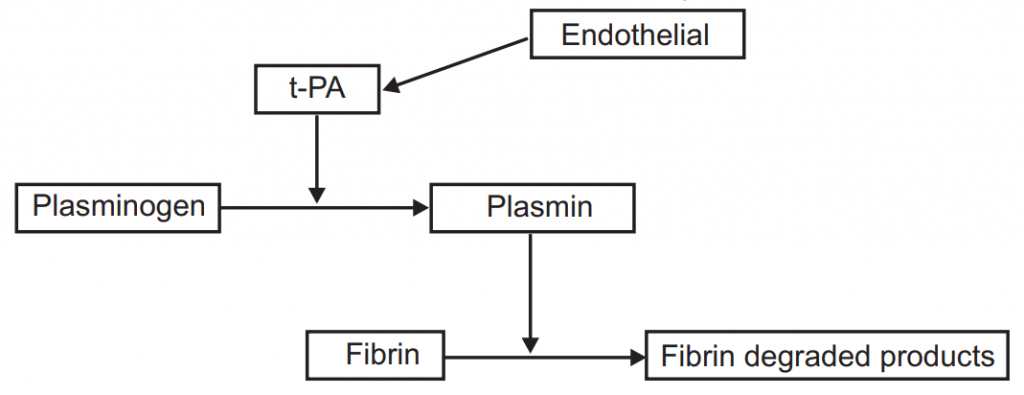
- The process of dissolution of a clot is called fibrinolysis.
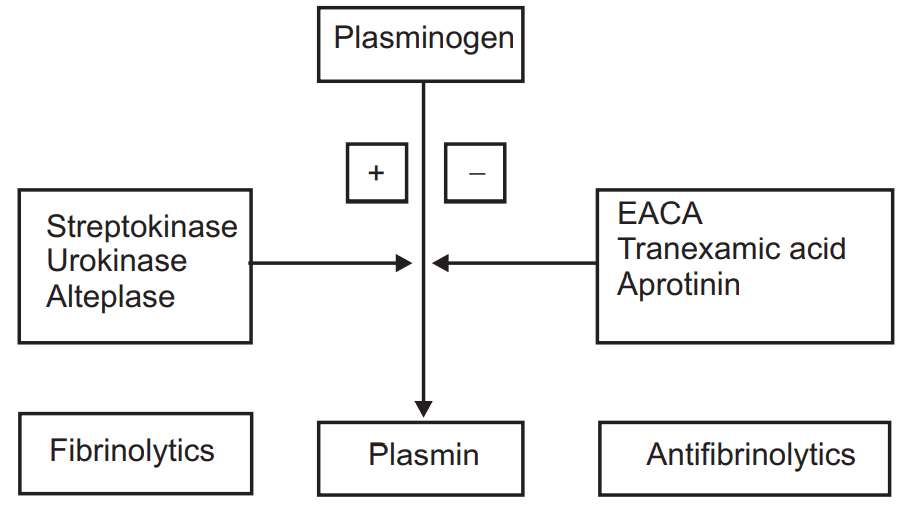
FIBRINOLYTICS
- Used to lyse the thrombi/clot to re-channelize the occluded blood vessel (mainly coronary artery).
- Work by activating the Fibrinolytic system:
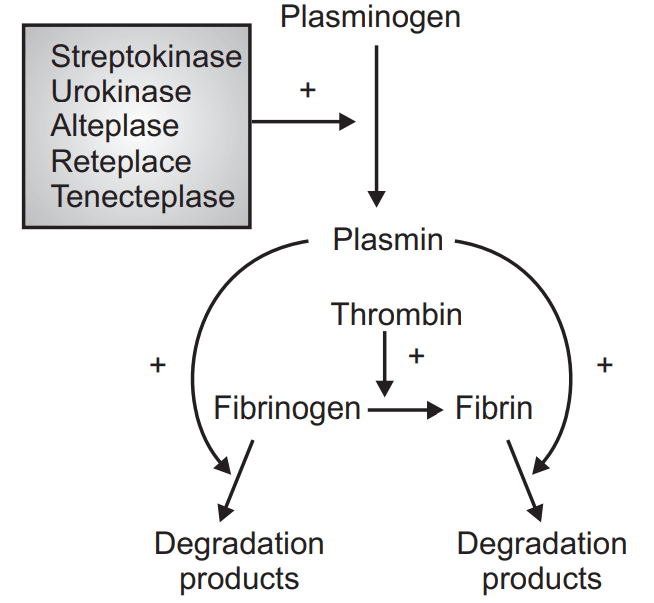
- STREPTOKINASE
- UROKINASE
- RETEPLASE (analogue of alteplase)
- ALTEPLASE (tissue – Plasminogen Activator [t-PA])
- TENECTEPLASE
Streptokinase:
- Obtained from – hemolytic streptococci.
- Binds with circulating plasminogen to form plasmin.
- A complex that activates plasminogen to plasmin.
- t½ = 30 − 80 min.
- Antigenic, Pyrogenic.
- Destroyed by circulating antistreptococcal antibodies.
- Hypotension and Arrhythmia can occur.
Uses:
- Acute myocardial infarction, – 7.5 to 15 lac IU; I.V over 1 hr period.
- Deep vein thrombosis, Pulmonary embolism.
Adverse Effects:
- Bleeding, hypotension, allergic reactions, fever, arrhythmias.
Contraindications:
- Recent trauma, surgery, abortion, stroke, severe.
- hypertension, peptic ulcer, bleeding disorders.
Urokinase:
- An enzyme isolated from human urine, now prepared from cultured human kidney cells.
- Direct plasminogen activator.
- t ½ of 10 to 15 min.
- Non-antigenic, Non-allergenic.
- Fever can occur but hypotension rare.
- Indicated in patients in whom streptokinase has been for an earlier episode.
Alteplase:
- Recombinant tissue Plasminogen Activator (rt-PA)
- Selectively activates plasminogen bound to fibrin
- Non-antigenic, not destroyed by antibodies
- Rapid acting, more potent
- Superior in dissolving old clots
- Short half-life 4-8 min
- Nausea, mild hypotension, fever may occur
- Expensive.
Newer Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activators:
Reteplase:
- Modified rt-PA.
- Longer half-life 15 -20 min, but less specific for fibrin bound plasminogen.
Tenecteplase:
- A genetically engineered mutant form of alteplase.
- Higher fibrin selectivity and longer half-life – 2 hrs. o Single bolus dose of 0.5 mg/kg sufficient.
- Very expensive.
Uses of Fibrinolytics:
- Acute myocardial infarction.
- Deep vein thrombosis.
- Pulmonary embolism.
- Peripheral arterial occlusion.
- Ischemic Stroke.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Anticoagulation