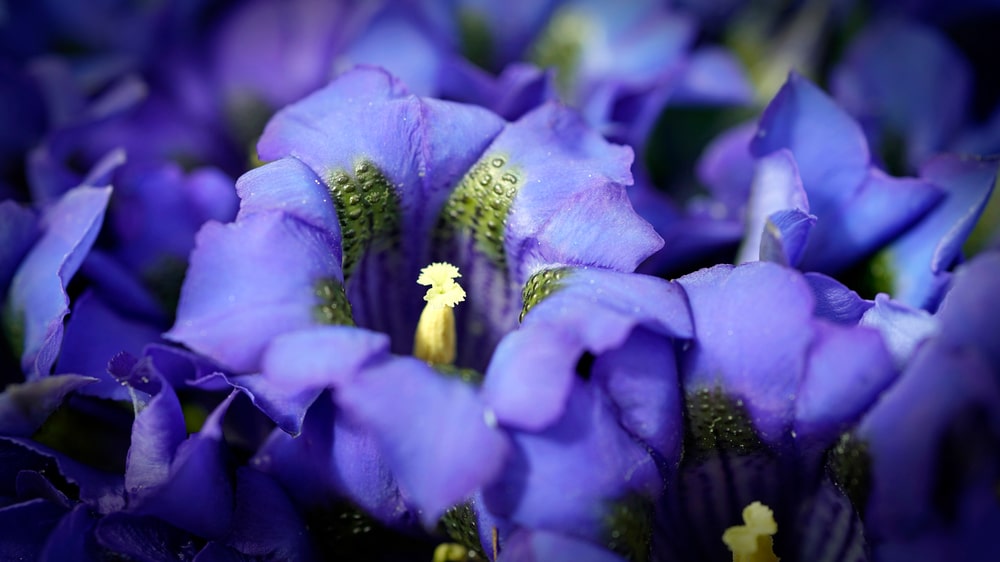
Synonyms: Gentian root, Gentiana, Radix Gentianae.
Biological source: Gentian consists of the dried fermented roots and rhizomes of Gentiana lutea, the yellow gentian.
Family: Gentianaceae.
Geographical source: Gentian is indigenous to hilly areas in Southern and Central Europe (like Jura, Vosges mountains), Yugoslavia, and Turkey.
Collection and Preparation of Gentian
Table of Contents
It is a perennial herbaceous tree and when the plants are 2 to 5 yrs old the turf i.e. a surface layer of earth containing grass plants with their matted root is carefully stripped off. The rhizomes and roots are dug up. This usually takes place from May to October. Collection in the autumn is more difficult because of the hardness of the soil but preferable from the medicinal point of view. At this stage, the pieces of roots and rhizomes are white without any odour which is unfermented gentian and have no demand in the market. Then the drug is made into heaps which are allowed to lie on the hillside for some time and may even be covered with earth. After it is washed and cut into suitable length, the drug is dried first in the open air and then in shades. Prepared in this way the drug became much darker in colour loses some of its bitterness and acquires a very distinctive odour.
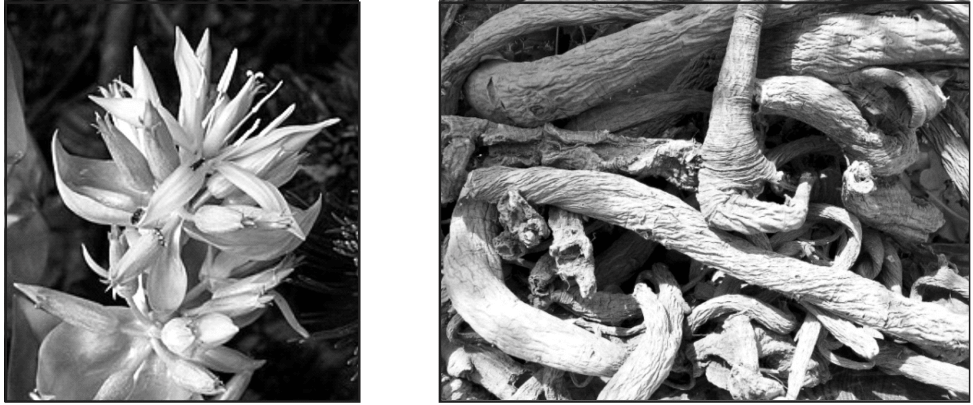

Macroscopical Character of Gentian
- Colour: Rhizomes are yellowish-brown.
- Odour: Special odour.
- Taste: Sweet taste followed by an intensely bitter taste.
- Shape: Cylindrical rhizome.
- Size: Diameter is about 4 cm and more than 1m in length.
- Fracture: Brittle, tough.
Constituents of Gentian
It contains bitter glycosides, alkaloids, yellow colouring matters, sugars, pectin and fixed oil. The bitter glycosides mainly contain gentiopicrin (also called gentiopicroside) which is a water-soluble crystalline compound with a bitter value of 12,000. During fermentation and drying, it breaks down into gentiogenin and glucose. A biphenolic acid ester of gentiopicroside, amarogentin which occur in a small amount (0.025-0.05 percent) has a bitterness value some 5000 times greater than that of gentiopicroside and is, therefore, an important constituent of the root. Other bitters isolated are sweroside and swertiamarin. The yellow colour of fermented gentian root is due to xanthones and gentisin (also known as gentiamarin) isogentisin and gentioside. It also contains gentisic acid and about 0.03 percent of the alkaloids gentianine and gentialutine. It is rich in sugars which include the trisaccharide gentianose, the disaccharide gentiabiose and sucrose which on fermentation can convert to glucose and fructose and for very long fermentation can convert into alcohol and CO2.
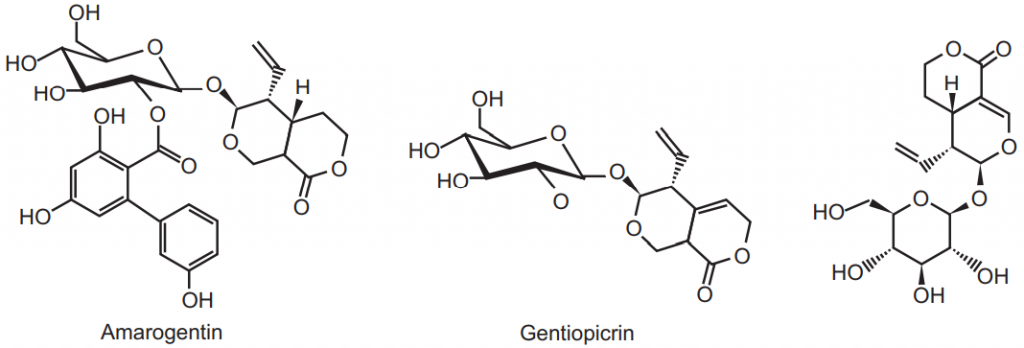
Chemical test: The extract shows blue fluorescence under UV light.
Uses of Gentian
Bitter tonic, stimulates gastric secretion, appetite enhancer. Gentian is used in herbal medicines for digestive problems, fever, hypertension, muscle spasm, parasitic worms, wounds, cancer, sinusitis, and malaria.
Adulterant and Substituent
- Rhizome of Rumex alpines
- Veratrum album,
- Gentiana purpurea
- Gentiana pannonica
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Bitter Almond
