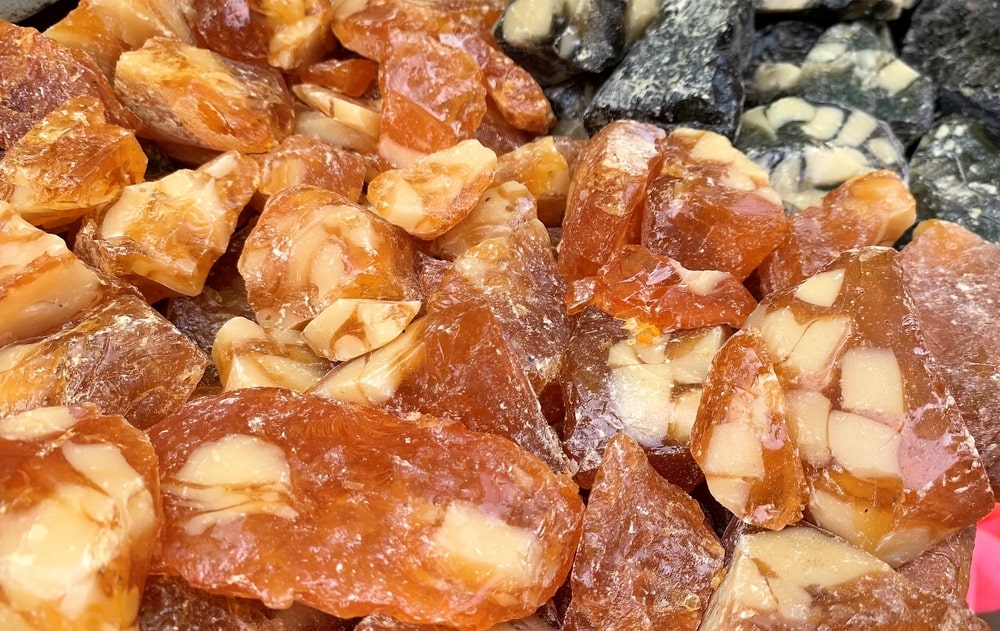
Synonym: Gum guggul, Scented bdellium.
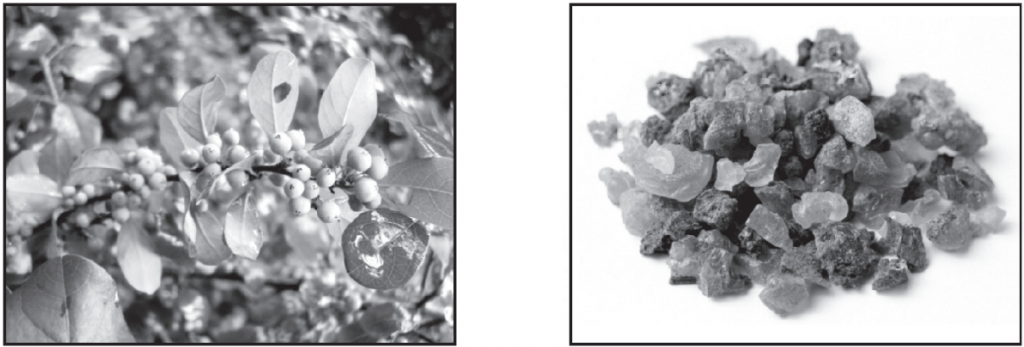
Biological source: Guggal belongs to the oleogum resin category and obtained from Commiphora weightii, Commiphora Mukul by making a deep incision at the basal part of stem bark.
Family: Burseracae.
Geographical source: It is a small to medium-size tree, native to African arid zones like Ethiopia, Somalia, Kenya, Zaire, and Zimbabwe and cultivated in Rajasthan, Haryana, and Gujarat.
Cultivation and Collection of Guggal
Table of Contents
The cultivation is mainly done by seeds and stem cuttings but seeds are more preferable. It grows well in sandy loam soil with a high amount of gypsum (pH 7 to 9). It is up to 2-4 meters in height occurs as a woody tree and shows spines cut branches on pale yellow to the brownish stem. The peels of bark are silvery and papery. In the arid and semiarid zones sloppy well-drained highly degraded lands are most preferred for cultivation. The seeds are collected from fully developed red berries from July to September because at this time the viability is more. The plant is raised through nursery beds and transplanted into the field after six months. The 25-30 cm long stem cuttings are planted in June or October, November for vegetative propagation. The resin is collected by making a deep circular incision on the stem of at least 5 years old plant. It is tapped and guggal secreted out as yellowish-white aromatic latex-like matter. The average yield is about 0.5-1 kg guggul per tree per year.
Description of Guggal
- Colour: Brown or pale yellow or dull green.
- Odour: Aromatic, balsamic, and Pleasant.
- Taste: Bitter and Characteristic.
- Size: 1 to 2.5 cm in diameter.
- Shape: Circular, irregular masses or agglomerated tears.
- Solubility: Forms white emulsion with water, partly soluble in alcohol.
Chemical Constituent of Guggal
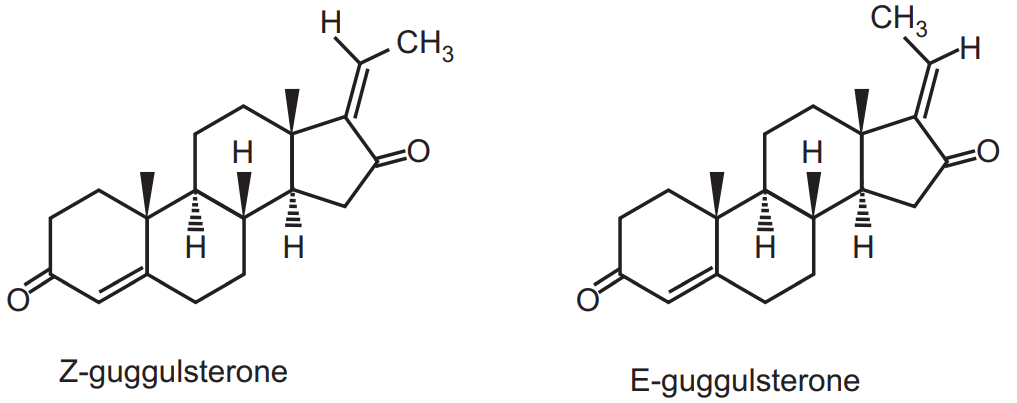
Major constituents are Guggulsterone E and Z, resin, gum, volatile oil and minor constituents are oleo gum resin which is a complex mixture of various classes of chemical compounds such as lignans, lipids, diterpene, steroids, etc. Other constituents like Guggulsterol I, II, III, and mukulol have been isolated from the drug. Quercitin, linoleic acid, oleic acid, stearic acid, palmitic acid, stigmasterol are other compounds. Upon steam distillation Guggal yields volatile oil which contains myrcene and caryophyllene. Pentosan, pentose, and furfural are the constituents of purified gum.
Chemical structure of Guggal
Guggulsterone Z, Guggulsterone E
Chemical test of Guggal
Add acetic anhydride to the ethyl acetate extract of guggul and boil it. After cooling add 2 ml of sulphuric acid which gives green colour at the junction of two liquids which confirms the presence of sterols.
Uses of Guggal
Guggul is used as an anti-inflammatory, hypolipidemic, antirheumatic, and hypocholesterolemic drug. Guggul extract lowers total lipid, serum cholesterol, and triglyceride level and reduces the serum p- lipoprotein level, and alters the lipoprotein ratio significantly. The Oleogum portion shows antiarthritic and anti-inflammatory activities. It also shows anti-obesity, Antiinflammatory, antiacne, platelet aggregation inhibition, and immunomodulatory effect.
Crude gum, oleo gum resin, alcohol extract, and petroleum ether extract have shown some side effects like skin rashes and diarrhea. It enhances the menstrual discharge so it should not be taken during pregnancy.
Adulterant: Commiphora species like C. abyssinica, C. roxburghii, C. molmol, and Boswellia serrata.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Benzoin
