Overview of Liliaceae
Habit: These are herbs and climbers, and rarely shrubs or trees with a bulb or rhizome, or with fibrous roots.
Leaves: These are simple, radical or cauline, or both.
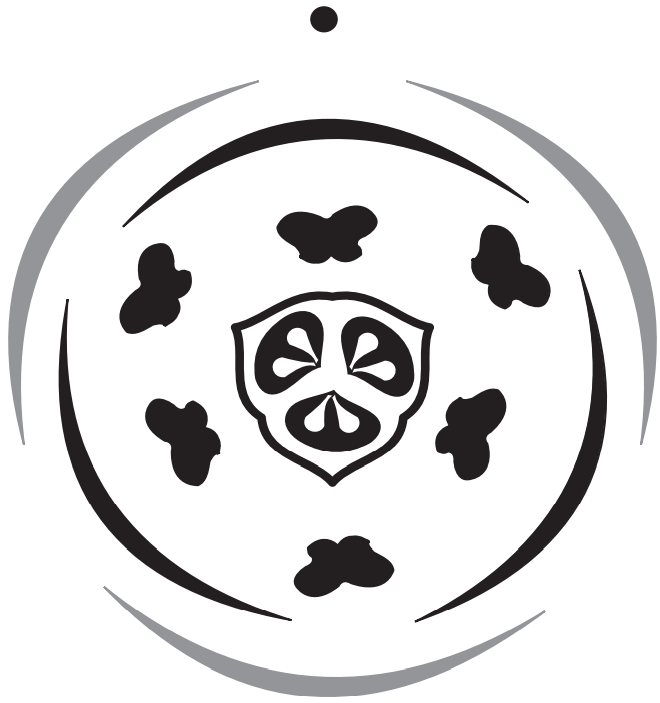
Flowers: The flowers are regular, bisexual (rarely unisexual) dioecious, as in smilex. They are trimerous and hypogynous. The bracts are usually small and scarious (thin, dry, and membranous).
Inflorescence: This may be a spike, raceme, panicle, or umbel, often on a scape.
Perianth: The perianths are petaloid. There are usually six in two whorls. They may be 3+3 and free (polyphyllous), or (3+3), and united (gamophyllous).
Androecium: There are six stamens in two whorls, 3+3, rarely free or united with the perianth (epiphyllous) at the base. The anthers are often dorsifixed.
Gynoecium: There are (3) carpels (syncarpous). The ovary is superior and three celled. There are usually ∞ ovules in two rows in each loculus. The placentation is axile. There are (3) or 3 styles.
Fruit: This may be a berry or capsule.
Seeds: The seeds are albuminous.
Floral formula:
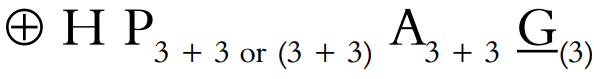

Examples: Onion, garlic, aloe, colchicum, etc.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Overview of Labiatae
