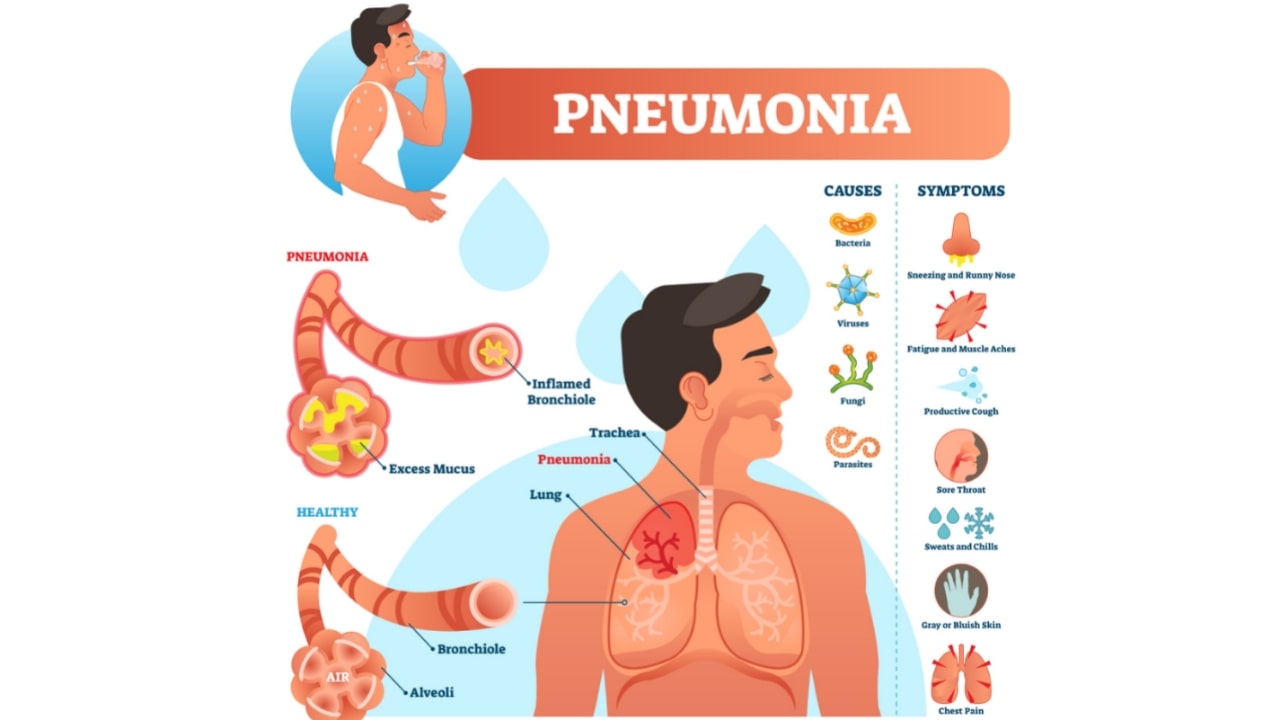
Definition: Pneumonia is an inflammatory lung condition that primarily affects the small air sacs known as alveoli. (Synonyms: Pneumonitis, Bronchopneumonia).
A common lung infection characterized by the accumulation of pus and other fluids in the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs is pneumonia. Structures that aid in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide are lung air sacs. In them, gathering pus makes it. difficult to breathe. Many kinds of micro-organisms (germs), including; bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, may cause pneumonia. These species get into the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes and breathing in this air contributes to contractions.
Epidemiology
Table of Contents
- About 450 million people worldwide (7 percent of the population) are affected by pneumonia, resulting in around 4 million deaths each year. In the 19th century, William Osler regarded pneumonia as “The captain of the men of death”. Survival increased with the advent of antibiotics and vaccines in the 20th century.
- Nevertheless, pneumonia remains a leading cause of death in developed countries and among the very old, the very young, and the chronically ill. Among those already close to death, pneumonia frequently shortens misery and thus has been named the “The old man’s friend”.
Agent/Factor: Viruses, Bacteria, and Fungi can all cause Pneumonia.
Host Factor: Age especially greater than 50 years, immunosuppressive therapy, bacteremia, intubated patients, etc.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to dust, fumes, and various chemicals.
Incubation Period: 2 to 4 weeks
Mode of transmission
- It may be transmitted by someone who is sneezing or coughing. Small droplets scatter in the air when an individual sneezes or coughs. The contagious organism produces certain droplets. They are then inhaled and can cause pneumonia in some instances. This is particularly relevant for individuals who are already ill with AIDS as a result of something like the flu or worse.
- However, in ways other than someone sneezing in your face, you might potentially get pneumonia. Bacteria or viruses that are already in your nose and throat will cure it. If these species spread from there to the lungs, they might cause pneumonia. Transmissible species cause pneumonia.
Symptoms
Symptoms of pneumonia may be mild to life-threatening. The most common pneumonia symptoms can include Cough (With Mucus), fever, chills, sweating and chest pain, shortness of breath.
- Symptoms of Viral pneumonia: Viral pneumonia such as; wheezing, can start with flu-like symptoms. After 12-36 hours, a high fever can occur.
- Symptoms Bacterial pneumonia: Along with profuse sweating, bluish lips and nails, and confusion, it can cause a fever as high as 105″ F.
Laboratory Diagnosis
Blood test, sputum examination, pulse oximetry, urine analysis, CT scan, etc.
Prevention and Control
Generally, It can be prevented by the Pneumonia vaccine (Prevnar 13, Pneumovax 23)
Home Treatment: Take prescribed drugs, take rest, drink plenty of water/fluids, etc.
Hospitalization: You will need to be treated if the symptoms are very serious or you have any health concerns. Physicians can keep track of the heart rate, temperature, and breathing at the hospital. Therapy can include IV Antibiotics administration, respiratory therapy, oxygen therapy, etc.
Other Prevention tips: In addition to vaccination, to prevent pneumonia, there are other things you should follow:
- Try to stop if you smoke. Smoking makes you pneumonia, to respiratory infections. more susceptible, especially to
- Daily, wash your hands with soap and water.
- Cover your coughs and sneezes and dispose immediately of the tissues used.
- To boost the immune system, maintain a balanced lifestyle. Get ample rest, eat a balanced diet, and exercise regularly.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Chikungunya