Aim: To perform the potentiometric titration of strong acid against a strong base.
Requirements:
- Apparatus: Beaker, Funnel, Pipette, Burrette, Titration flask.
- Chemicals: Sodium chloride, Ammonium thiocynate.
Theory:
Potentiometric titration is a technique similar to the direct titration of a redox reaction. It is a useful means of characterizing an acid. No indicator is used; instead, the potential is measured across the analyte, typically an electrolyte solution. To do this, two electrodes are used, an indicator electrode (the glass electrode and metal ion indicator electrode) and a reference electrode. Reference electrodes generally used are hydrogen electrodes, calomel electrodes, and silver chloride electrodes. The indicator electrode forms an electrochemical half cell with the interested ions in the test solution. The reference electrode forms the other half cell.
The overall electric potential is calculated as Ecell = Eind − Eref + Esol. Esol is the potential drop over the test solution between the two electrodes. Ecell is recorded at intervals as the titrant is added. A graph of potential against volume added can be drawn and the endpoint of the reaction is halfway between the jump in voltage. Ecell depends on the concentration of the interested ions with which the indicator electrode is in contact. For example, the electrode reaction maybe
Mn+ + ne− → M
As the concentration of Mn+ changes, the Ecell changes correspondingly. Thus the potentiometric titration involves measurement of Ecell with the addition of titrant. Types of potentiometric titrations: acid-base titration (total alkalinity and total acidity), redox titration (HI/HY and cerate), precipitation titration (halides), and complexometric titration.
Procedure:
Take 50 ml of 0.1 M HCl. Add ml wise 0.1 M NaOH solution in an acid-containing flask. After the addition of NaOH, measure the pH by pH meter.
Plot a graph of ml of NaOH Vs pH and locate the equivalent point.
Observation Table:
| Sr.No. | ml of NaOH (B.R) | pH |
Graph:
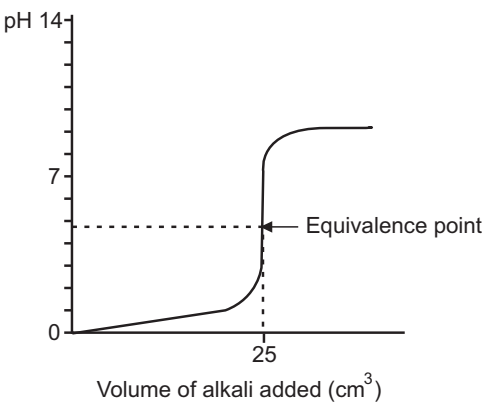
Result: The normality of sodium hydroxide is …… N.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Conductometric Titration of Strong Acid Against Strong Base
