Research is defined as careful consideration of study regarding a particular concern or problem using scientific methods.
Research is also defined as a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict, and control the observed phenomenon.
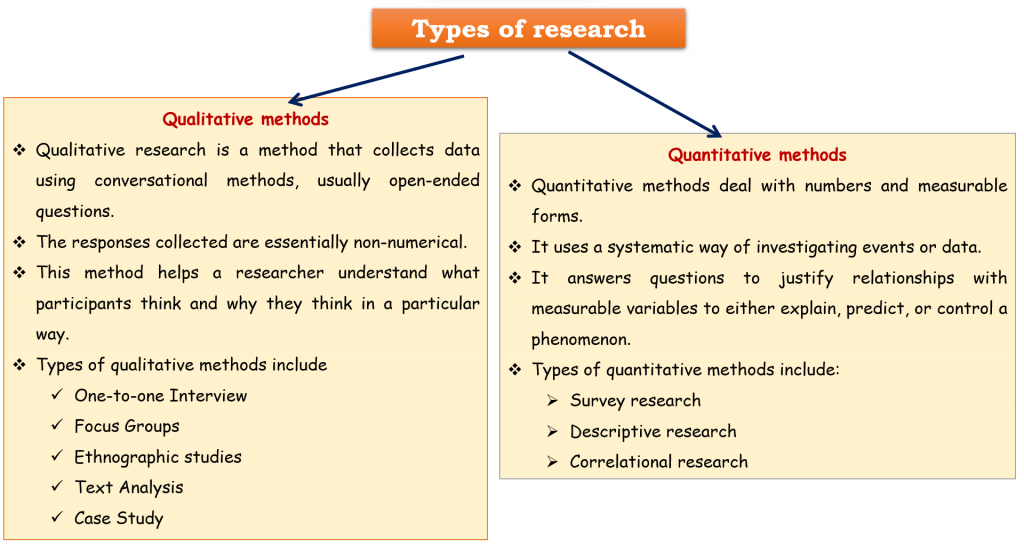
It involves inductive and deductive methods.
- Inductive research methods analyze an observed event, and approaches are associated with qualitative research.
- Deductive methods verify the observed event and are more commonly associated with quantitative analysis.
Need for Research:
Table of Contents
- Identify potential and new customers
- Understand existing customers
- Set pragmatic goals
- Develop productive market strategies
- Address business challenges
- Put together a business expansion plan
- Identify new business opportunities
Purpose of Research:
Exploratory
- As the name suggests, researchers conduct exploratory studies to explore a group of questions.
- The answers and analytics may not offer a conclusion to the perceived problem.
- It is undertaken to handle new problem areas that haven’t been explored before.
- This exploratory process lays the foundation for more conclusive data collection and analysis.
Descriptive
- It focuses on expanding knowledge on current issues through a process of data collection.
- Descriptive research describes the behavior of a sample population.
- Only one variable is required to conduct the study.
- The three primary purposes of descriptive studies are describing, explaining, and validating the findings.
- For example, a study was conducted to know if top-level management leaders in the 21st century possess the moral right to receive a considerable sum of money from the company’s profit.
Explanatory
- Causal or explanatory research is conducted to understand the impact of specific changes in existing standard procedures.
- Running experiments is the most popular form.
- For example, a study that is conducted to understand the effect of rebranding on customer loyalty.
Characteristics of Research:
- Good research follows a systematic approach to capture accurate data.
- Researchers need to practice ethics and a code of conduct while making observations or drawing conclusions.
- The analysis is based on logical reasoning and involves both inductive and deductive methods.
- Real-time data and knowledge is derived from actual observations in natural settings.
- There is an in-depth analysis of all data collected so that there are no anomalies associated with it.
- It creates a path for generating new questions.
- Existing data helps create more research opportunities.
- It is analytical and uses all the available data so that there is no ambiguity in inference.
- Accuracy is one of the most critical aspects of research.
- The information must be accurate and correct.
- For example, laboratories provide a controlled environment to collect data. Accuracy is measured in the instruments used, the calibrations of instruments or tools, and the experiment’s final result.
Common steps in Research:
Observations and formation of the topic
- Consists of the subject area of one’s interest and following that subject area to conduct subject-related research.
- The subject area should not be randomly chosen since it requires reading a vast amount of literature on the topic to determine the gap in the literature the researcher intends to narrow.
- A keen interest in the chosen subject area is advisable.
- The research will have to be justified by linking its importance to already existing knowledge about the topic.
Hypothesis
- A testable prediction that designates the relationship between two or more variables.
Conceptual definition
- Description of a concept by relating it to other concepts.
Operational definition
- Details in regards to defining the variables and how they will be measured/assessed in the study.
Gathering of data
- Consists of identifying a population and selecting samples, gathering information from or about these samples by using specific research instruments.
- The instruments used for data collection must be valid and reliable.
Analysis of data
- Involves breaking down the individual pieces of data to conclude it.
Data Interpretation
- This can be represented through tables, figures, and pictures, and then described in words.
Test, revising of hypothesis
Conclusion, reiteration if necessary
Introduction to Research: Need for research, Need for the design of Experiments. Experiential Design Technique, plagiarism.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Statistics And Biostatistics
