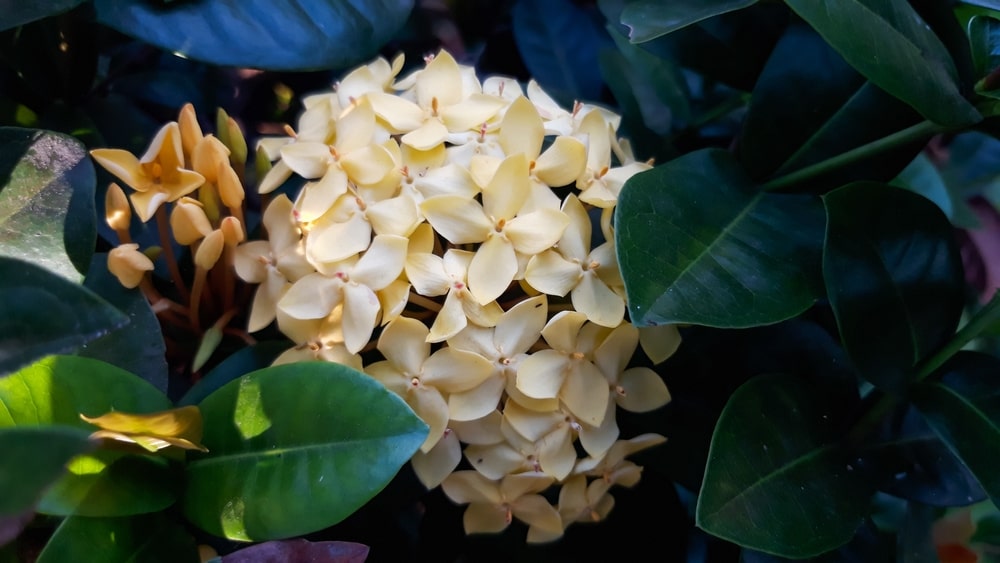
Characteristics of Rubiaceae
Habit: These are herbs (erect or prostrate), shrubs, trees, and climbers, sometimes thorny.
Leaves: The leaves are simple, entire, opposite (decussate) or whorled, with interpetiolar (sometimes intrapetiolar) stipules.
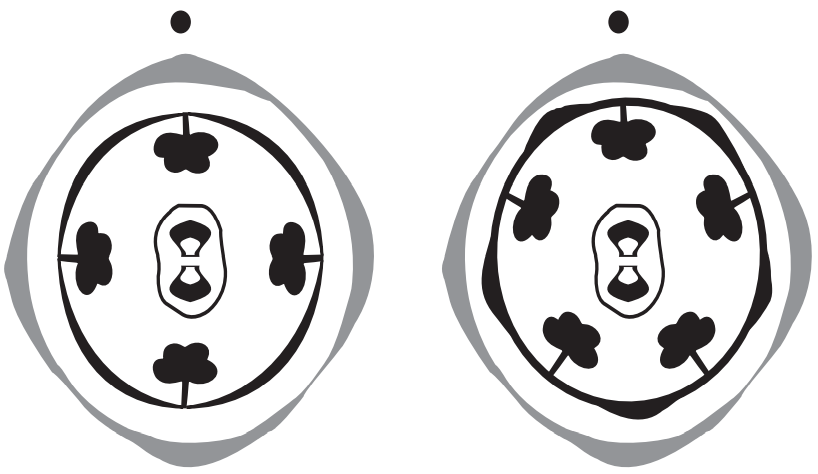
Flowers: The flowers are regular, bisexual, epigynous, sometimes dimorphic, as in some species of randia and oldenlandia.
Inflorescence: The inflorescence is typically cymose, frequently dichasial and branched, sometimes in globose heads.
Calyx: There are usually four sepals, sometimes five. It is gamosepalous. The calyx tube adnate to the ovary.
Corolla: There are usually four sometimes five. It is gamopetalous, generally rotates. The aestivation is valvate, imbricate, or twisted.
Androecium: The stamens are epipetalous, inserted within or at the mouth of the corolla tube, alternating with the corolla lobes.
Gynoecium: The carpels are two, syncarpous. The ovary is inferior, commonly two-locular, with 1-∞ ovules in each. The disc is usually annular, at the base of the style.
Fruit: The fruit is a berry, drupe, or capsule.
Seeds: The seed has fleshy or horny endosperm.
Floral formula:
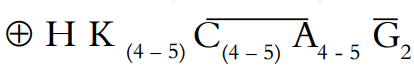
Examples: Cinchona, Ipecac, etc.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Characteristics of Liliaceae
