In steam distillation, impure compounds are distilled with the help of steam. This method applies to solids as well as liquids. For purification by steam distillation, an impure compound should not decompose at the steam temperature, should have a fairly high vapor pressure at 373 K, should be insoluble in water and the impurities present should be non-volatile.
Steam Distillation Principle:
Table of Contents
A mixture of immiscible liquids begins to boil when the sum of their vapour pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure. Let Pi represent the vapour pressure of water and p2 the vapour steam distillation the liquid boils at a temperature at which pressure of the organic liquid. In
Pi+ P2 Atmospheric Pressure
This temperature must be lower than the normal boiling point of water or the organic liquid. Thus in steam distillation, the impure liquid boils at a temperature that is lower than its normal boiling point.
Construction:
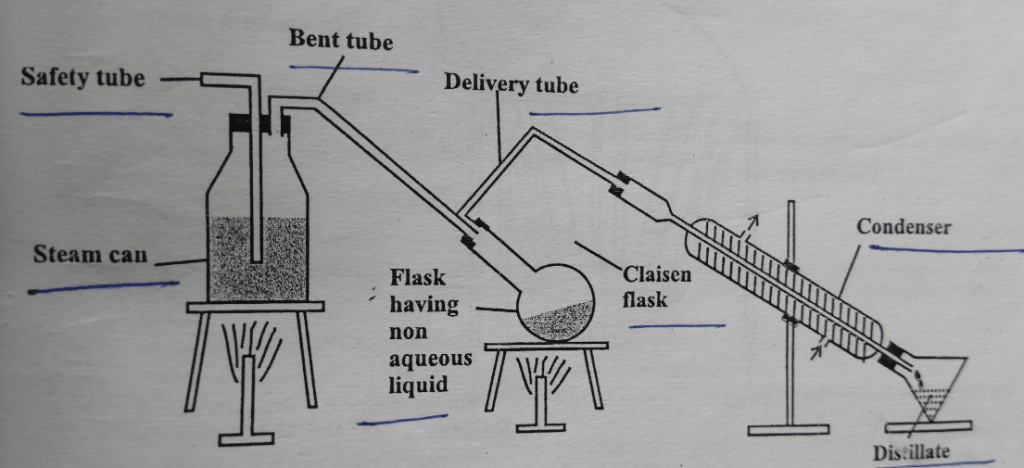
It consists of steam can with two holes. Through one hole safety tube passes to relieve pressure if high pressure generated. Through other holes, a bent tube is passed whose other end is attached to the flask having non-aqueous liquid. There is also a provision to heat steam can and flask. A delivery tube is also attached to the flask and condenser. The condenser is attached to the receiver.
Working of Steam Distillation:
The steam can is filled with water. The non-aqueous liquid is placed into a flask and a small quantity of water is added. The flask is then heated gently. Now steam is bubbled through the contents in the flask. The vapors of the compound mix up with steam and escape into the condenser. The condensate thus obtained is a mixture of water and non-aqueous liquid which can be separated.
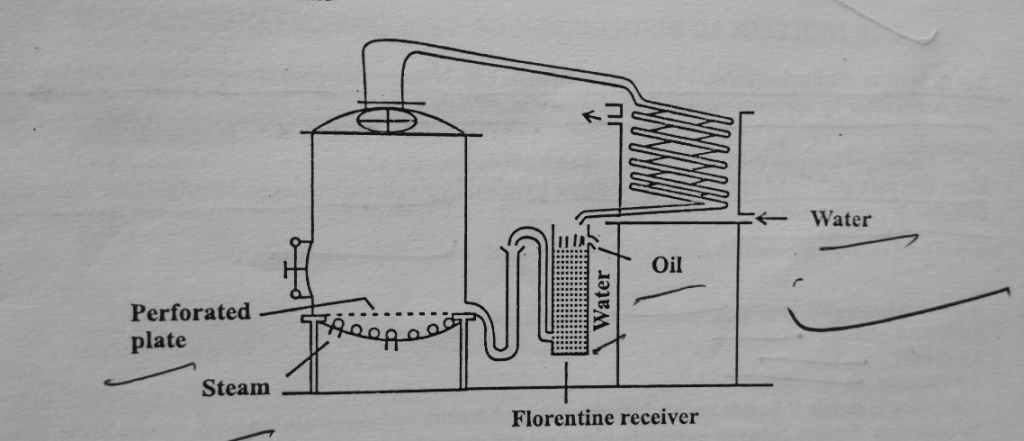
It consists of a still having a mesh or perforation near the bottom. Steam is produced by boiling water below the mesh. The steam passes through the materials (to be extracted) packed over the mesh. The vapor containing the volatile oil is then passed to the condenser. The distillate is collected in Florentine receivers. Florentine receiver separates the oil and water according to their densities. The aqueous phase can be recycled again to avoid the loss of volatile oil in the water.
Florentine Receiver is of two types: Type-I is used for the separation of oil heavier than water. While Type-II is used for the separation of oil lighter than water. In Type-I receiver, the tap fitted near the bottom of the vessel is used for collecting oil, whereas the tap fitted near the top of the vessel is used for water to overflow. In Type-II receiver is fitted with a siphon at the bottom that works when it gets filled with water whereas the tap fitted near the top is an outlet for the flow of oil.
Use:
- Steam distillation is used for the separation of inadmissible liquids
- This method is used for the extraction of volatile oils such as clove, eucalyptus.
Advantages:
- Steam distillation is useful for extracting most fats, oils, and waxes. This process works well for types of substances that do not mix with water.
- Steam distillation is used for oil extraction and also used in the fragrance and essential oil industry
Disadvantage:
- Steam distillation has the disadvantage of having a higher initial cost for investment in the equipment.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Fractional Distillation