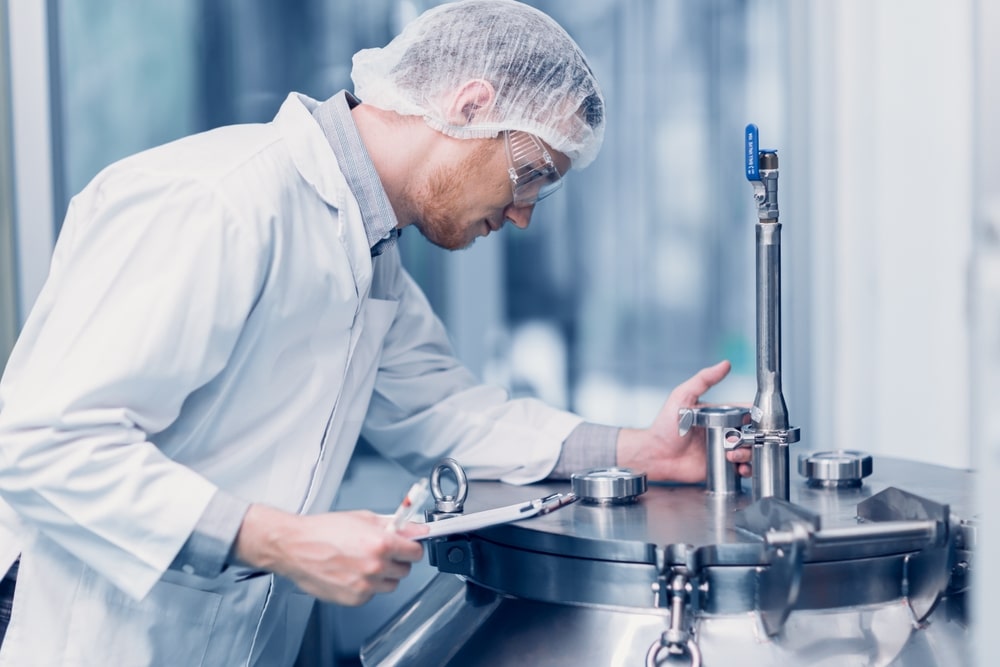
Aim:
To check the sterility of Water for injection (WFI) by direct inoculation method.
Requirements:
Fluid thioglycollate medium, alternative thioglycollate medium, soyabean casein digest medium, test tubes (large size), conical flask, glass marking pencil, laminar airflow, etc.
Principle:
A sterility test must be carried out under aseptic conditions designed to avoid accidental contaminations of the product during testing by using a laminar airflow cabinet. A fluid thioglycollate medium is used for clear fluid products for aerobic as well as anaerobic bacteria. Alternative thioglycollate medium is used for turbid and viscid products and for devices having tubes with small lumina for checking the growth of bacteria. Soyabean-casein digest medium is suitable for the culture of both fungi and aerobic bacteria. All media used for the test should comply with the test for sterility and growth promotion test.
Sterility tests can be performed by method A (membrane filtration) or method B (direct inoculation). The given sample or water for injection not having any antimicrobial activity hence, nor required for the inactivation of a given sample. The given sample quantity is also less than 100 ml. Hence method B: direct inoculation should be used.
Procedure:
Prepare the specific quantity of media (FTM or ATM and SCDM) for the test as per guidelines given in IP 2014 and based on sample size. The external surface of ampoules and closures of vials should be cleaned with a suitable antimicrobial agent. Remove the sample from the test container with a sterile pipette or with a sterile syringe or a needle. Transfer the quantity of the preparation under examination prescribed in IP 2014 directly into the culture medium under aseptic conditions. Incubate sample containing FTM or ATM at 30 to 35°C and SCDM at 20 to 25°C for not less than 14 days. Observe the test tubes (Fig.1) of media periodically during the 14 days of incubation.
Observations and Results:
Observe the media for macroscopic evidence of microbial growth. If no evidence of microbial growth is found, then the preparation complies with the test for sterility. If evidence of microbial growth is found, then the preparation does not comply with the test for sterility. If the test is invalid then repeat the test with the same number of units as in the original test. The test may be considered invalid if microbial growth is found in the negative controls or data on microbial monitoring of the sterility testing facility show a fault or a review of the testing procedure used for the test in question reveals a fault or after identifying the microorganisms isolated from the containers showing microbial growth, the growth may be ascribed without any doubt to faults concerning the materials or technique used in conducting the test procedure.
Note:
- The test must be carried out under aseptic conditions designed to avoid accidental contaminations of the product during testing.
- If the preparation under examination has antimicrobial activity, carry out the test after neutralizing this with a suitable neutralizing substance or by dilution in a sufficient quantity of culture medium.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Isolation of Pure Culture by Streak Plate Method
