Sunscreen Preparation: Sunscreen, also known as sunblock, sun cream, or suntan lotion, is a lotion, spray, gel, foam (such as an expanded foam lotion or whipped lotion), stick, or other topical product that absorbs or reflects some of the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation and thus helps to protect against sunburn.
- The purpose of sunscreen is to either scatter sunlight effectively or to absorb the erythema part of the sun’s radiation.
- Diligent use of sunscreen can also slow or temporarily prevent the development of wrinkles, moles, and sagging skin.
- The use of sunscreen preparation has attained importance in the cosmetic field suntan preparation is divided into three classes
- Preventive
- Simulatory
- Therapeutic
- Sunburns may be prevented by the shading of the surface of the body as well as by the use of the chemicals that screen out certain rays of the sun.
Classification of Sunscreens
Table of Contents
- Chemical sunscreens (i.e., those that absorb the UV light)
- Physical sunscreens (i.e., those that reflect the sunlight)
1. Chemical (Organic) Sunscreens:
- Organic UV filters are active ingredients that absorb UV radiation within a particular range of wavelengths, depending on their chemical structure.
- Once the UV filter absorbs energy, it moves from a low-energy ground state to a high-energy excited state.
2. Inorganic (Physical) Sunscreens:
- Zinc oxide
- Titanium dioxide
- Others: iron oxide, petrolatum, kaolin, calamine, Ichthammol (Aluminum Bituminosulfate), talc.
- Inorganic agents function by reflecting, scattering, or UV radiation (Opaque)
- Their opaque nature and “whitening effect” are an inherent disadvantage, which may be minimized by the use of micronized or ultrafine particles.

Benefits of Sunscreen
- Sunscreen use can help to prevent melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
- There is little evidence that it is effective in preventing basal cell carcinoma.
- Sunscreen can slow or temporarily prevent the development of wrinkles and sagging skin.
- Reduces skin discoloration.
- Skin lighting benefits.
- High UVA and UVB protection.
- Prevention of brown spots and pigmentation,
- Protection against pollutants.
Ideal Characteristics of Sunscreen
- It should absorb arrhythmogenic radiations in the range of 290-320 nm without its breakdown.
- It should allow full transmission of radiation in the range of 300-400 nm for the tanning effect.
- It should be non-volatile.
- It should have suitable solubility characteristics in a suitable vehicle.
- It should be stable to heat, light, and perspiration.
- It should be mild or odorless.
- It should be non-toxic, non-irritant, and non-sensitizing.
- It should be capable of retaining its sun screening property for several hours.
- It should not stain the body.
- It should be neutral.

Sunscreen Preparation
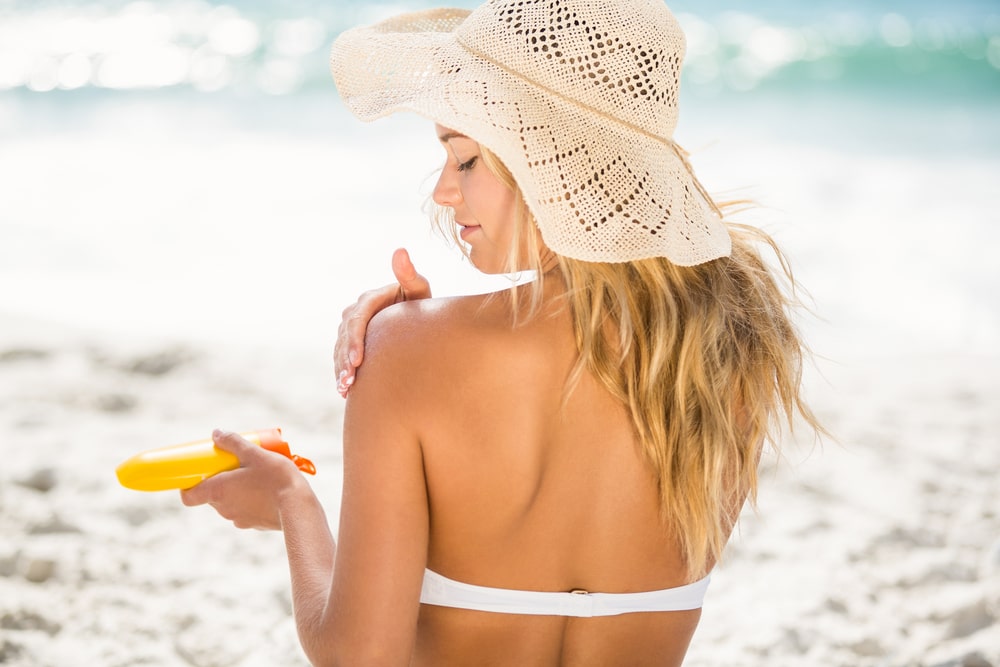
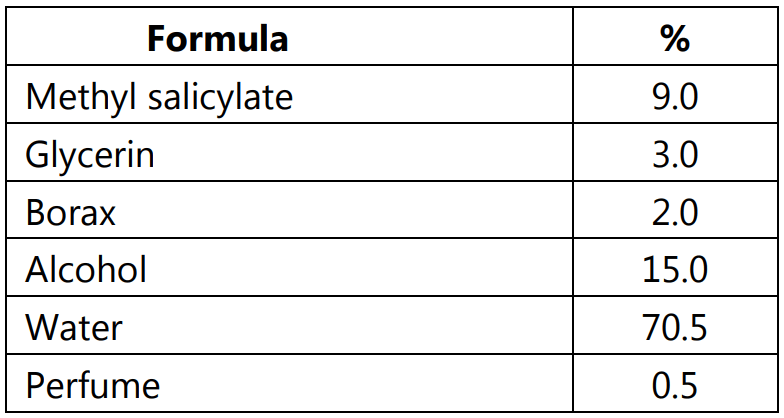
1. Sunscreen Lotion (Solution Type):
Method:
- Heat the water, dissolve the borax in it and add the salicylate.
- Stir until dissolved.
- Mix the perfume with the alcohol, add the glycerin and stir this into the methyl salicylate solution.
- Filter, if it is desired to color the solution, add a sufficient quantity of alcohol-soluble colorant.
2. Sunscreen Cream:

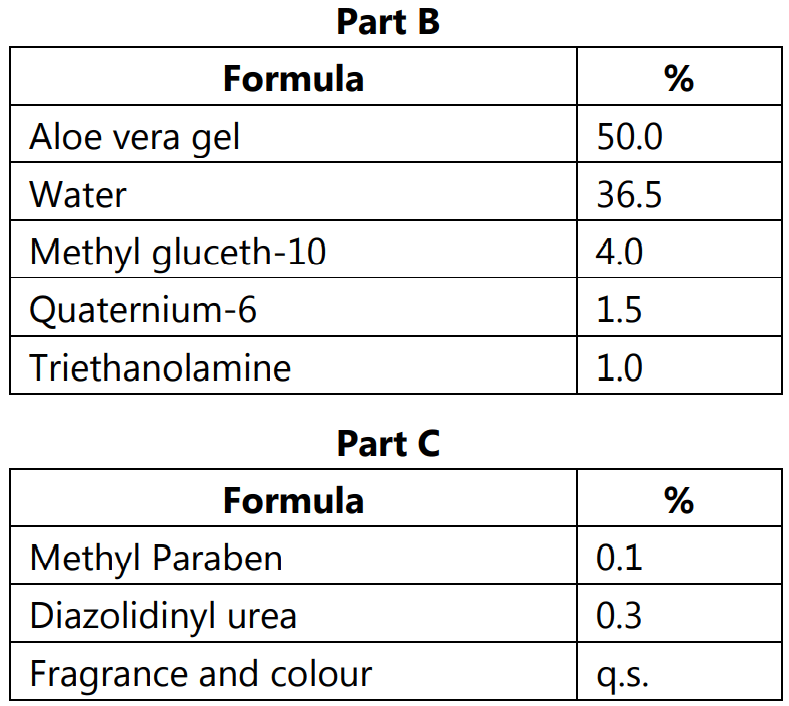
Method:
- Heat part (A) and part (B) separately to 70o C
- Add (B) to (A) with mixing.
- Let it cool to approximately 45-50 oC.
- Add preservative, Diazolidinyl urea, and fragrance.
- SPF is approximately 8-10.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Formulation and Evaluation of Toothpaste
