Common Name: Lanolin, purified wool fat.
Biological Source: It is a yellow waxy substance secreted by the sebaceous glands of wool-bearing animals like sheep, Ovis aries.
Family: Bovidae.
Geographical Location: Commercially it is prepared in New Zealand, Australia, the USA and India.
Method of Preparation: Sheep’s wool contains about 45% of a fat known as suint, which must be removed. Crude lanolin is separated by washing with sulphuric acid and then purified and bleached. The product is known as anhydrous lanolin or wool fat. Further, the hydrous wool fat is produced by intimately mixing wool fat with 30% of water.
Physical Properties:
- Colour: Whitish yellow
- Odour: Characteristic
- Taste: Bland
- Solubility: Insoluble in water but forms turbidity with ether and chloroform
- Melting-point: 40° to 44.4°C
- Saponification value: 92 – 106
- Iodine value: 18 – 35
- Acid value: Less than 1
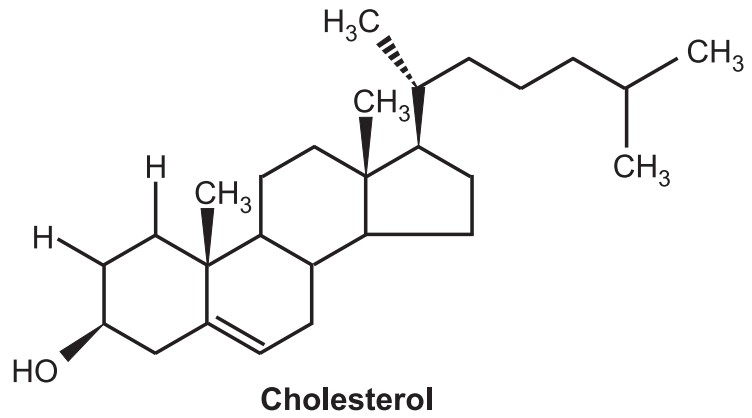
Chemical Constituents: It contains alcohols, cholesterol, and is cholesterol, together with various esters. Hydrous wool fat also contains acids in combination with lanoceric, lanopalmitic, carnaubic, myristic, oleic, cerotic, and palmitic acids. It contains 50% of water.
Chemical Tests:
- 1 g of wool fat is boiled with 20 ml of alcohol and the solution is filtered and cooled, the filtrate should not be rendered turbid by the addition of a 5% alcoholic solution of silver nitrate. This indicates the absence of chlorides.
- 1 g of the fat is dissolved in 3 or 4 ml of acetic anhydride and few drops of sulphuric acid are added. An initial pink colour changes to green and then finally blue. This indicates the presence of cholesterol.
- When a 2% solution in chloroform is gently poured over the surface of concentrated sulphuric acid, it gradually develops a purple-red colouration at the junction of the liquids.
- 10 g of wool fat is heated with 50 ml of water in a water bath. The aqueous layer on filtration should not yield glycerin on evaporation, and when boiled with potassium hydroxide should not evolve the odour of ammonia. This indicates the absence of nitrogenous organic matter.
Uses: It is used as a moisturizer to treat dry, rough, scaly, itchy skin and minor skin irritations. It is mainly used as a water absorbable ointment base. Lanolin is often used as a raw material for producing cholecalciferol using irradiation (vitamin D).
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Castor Oil
