What’s Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Table of Contents
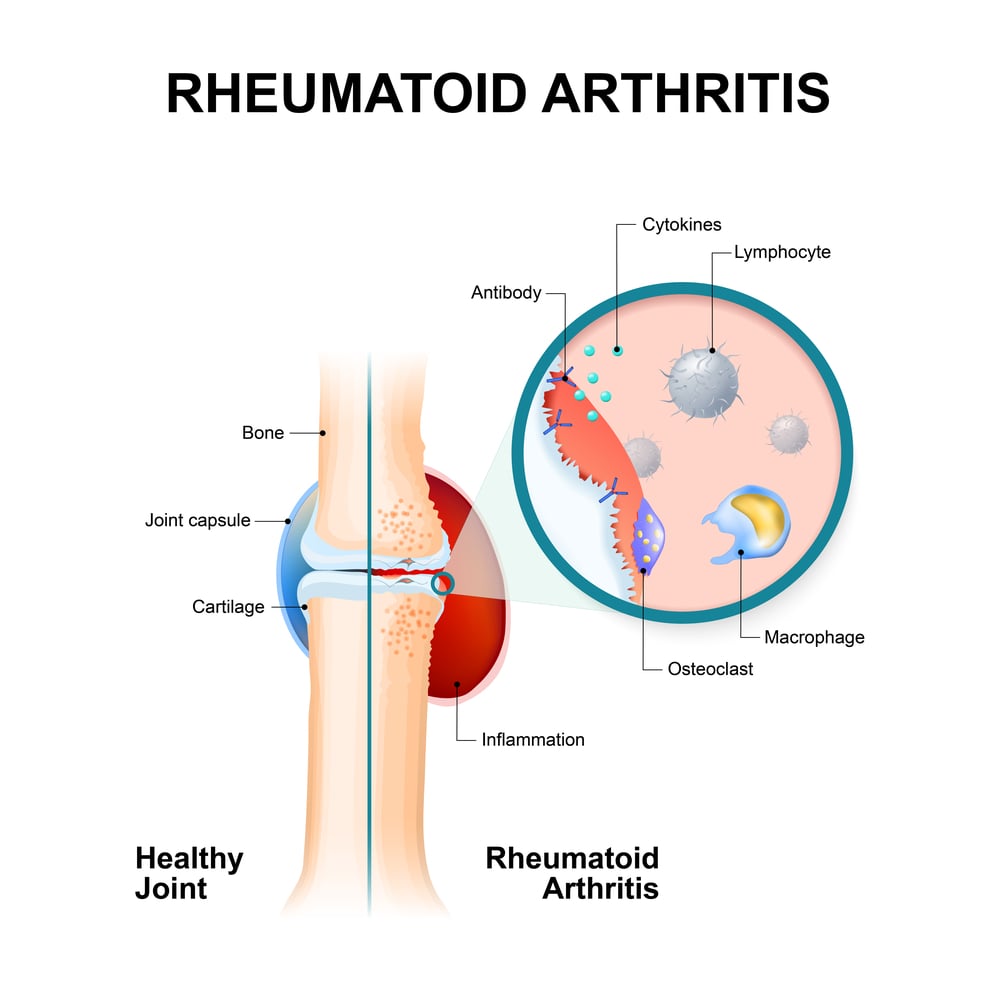
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the normal immune response is directed against an individual’s tissue, including the joints, tendons, and bones, resulting in inflammation and destruction of these tissues.
- Attacks normal joint tissues, causing inflammation of the joint lining (synovial joint).
- It is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints.
- Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body.
- The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and increases with age, approaching 2% and 5% in men and women, respectively, by age 65.
- The incidence also increases with age, peaking between the 4th and 6th decades. The annual incidence for all adults has been estimated at 67 per 100,000.
- Both prevalence and incidence are 2-3 times greater in women than in men. Genetic factors have an important role in the susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms:
- Fatigue, Joint pain, Joint Swelling, Joint Redness, Joint warmth, Stiffness of joints in the morning, Fever, Weight loss.
Drugs Used To Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
- Biological Response Modifiers(Biologics).
- Glucocorticosteroids.
1. Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
- They are mainly of two types:
(a) Non-selective Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors: Aspirin, Ibuprofen.
(b)Selective Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitors: Nimesulide, Meloxicam.
MOA:
- NSAIDs reduce inflammation and pain but it does not have any effect on disease progression.
- Inhibits pain sensation-Analgesic action.
- Reduced capillary permeability, Decreased tissue edema-Anti inflammatory action.
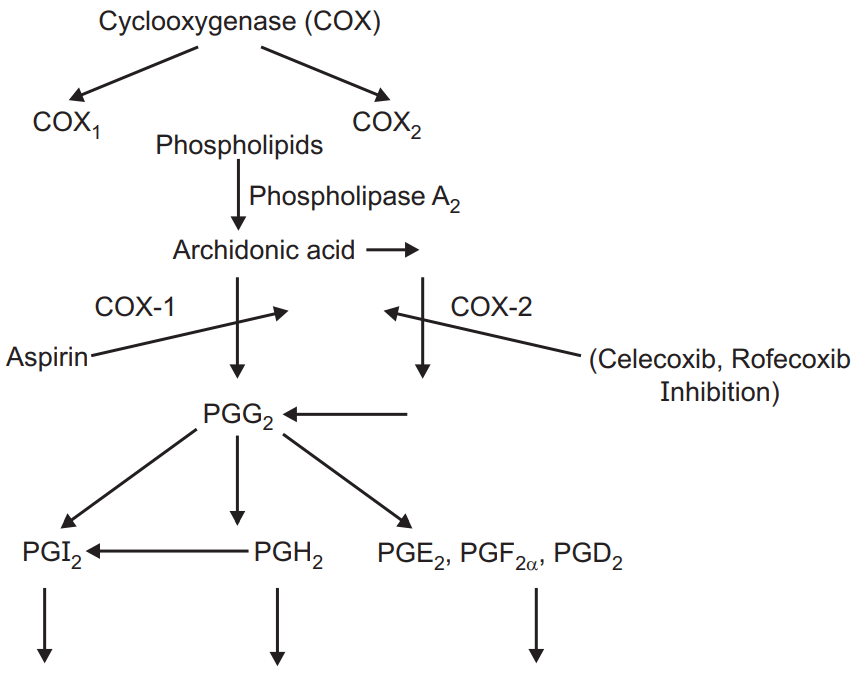
- These release Prostaglandins which are responsible for inflammation, pain, etc.
- COX inhibitors cause inhibition of COX enzyme and inhibit the conversion of arachidonic acid into PGG2 later PGG2 to PGH2, PGI2, PGE2, PGF2α, and PGD2. So result: Inhibits pain sensation-Analgesic action, Decreased tissue edema-Anti inflammatory action.
Adverse Effects:
- Nausea, Vomiting, Constipation, Diarrhea, Dizziness, Edema, Kidney failure, Ulcers.
2. Disease-Modifying Anti Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
- The effects of these drugs take few weeks to several months to become evident, so they are also called Slow Acting Anti Rheumatic (SAARDs).
- Drugs (SAARDs): Methotrexate, Sulphasalazine, Chloroquine, Gold compounds, etc.
Methotrexate:
MOA:
- It is a folate antagonist.
- It inhibits the chemotaxis of neutrophils.
- Hence, the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines is reduced and cell-mediated immunity is suppressed.
ADR:
- Nausea, Vomiting, Mucosal ulcers.
- It is used in a very low dose and is contraindicated in pregnancy, liver disease, and peptic ulcers.
Sulphasalazine:
MOA:
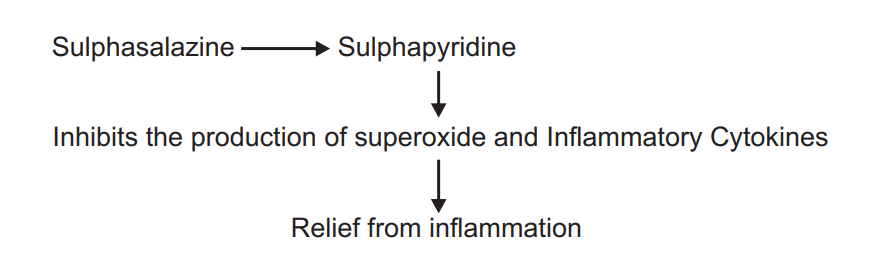
ADR:
- Nausea, Vomiting, Headache, Diarrhea, Skin rashes.
3. Biologics:
- These are preparations made from organisms or their products.
- They are administered parentally.
- They are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis which does not respond to DMARDs.
Etanercept:
MOA:
- TNF alpha antagonist.
- TNF alpha is a potent inflammatory cytokine.
- TNF alpha antagonists reduce or inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines hence produce relief from inflammation.
Anakinra:
MOA:
- Interleukins 1(IL-1) antagonist.
- IL -1 is also a pro-inflammatory cytokine.
- IL-1 antagonist reduces or inhibits the pro-inflammatory cytokine hence produce relief from pain.
Abatacept:
MOA:
- T-cell Modulating Agent.
- It prevents and cures the infection.
Rituximab:
MOA:
- B-Lymphocyte Depletion.
- Destroy the B cells with rheumatoid arthritis.
ADR:
- Prolonged use leads to tuberculosis, urinary tract infection.
4. Glucocorticosteroids.
- The drugs are Prednisolone, Triamcinolone.
MOA:
- Inhibits gene transcription of COX2, cytokines, interleukins as a result produce relief from inflammation.
- Increase release and synthesis of annexin-1, which is potent anti-inflammatory to cells hence produce anti-inflammatory actions.
ADR:
- Prolonged use leads to toxic effects.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Anti-Gout Drugs