Aim: To record blood pressure.
Requirements: Stethoscope, Mercury Sphygmomanometer.
(a) Stethoscope is an instrument used for listening to sound produced inside the body with amplification. The commonly used stethoscope consists of:
- Ear frame consists of two curved metallic tubes joined together with a flat ‘U’ shaped spring which keeps them pull together.
- Conducting tubes are simple flexible and soft pressure tubes of rubber or latex material.
- Chest piece consists of a bell and flat diaphragm which causes an amplification of the body sound.
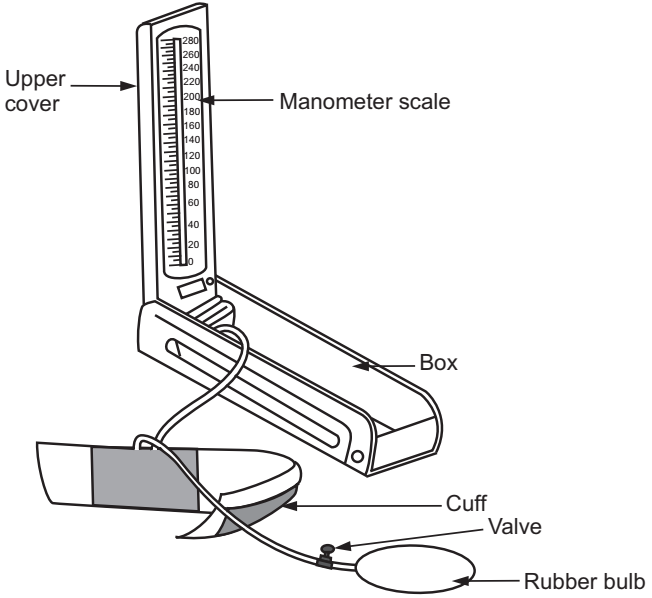
(b) Sphygmomanometer (“Sphygmo” means “pulse”; “Manos” means “thin” and “metro” means “measure”). It is the instrument used for recording arterial blood pressure in humans. It consists of:
- A Mercury manometer is fitted inside the lid of the instrument. It consists of a mercury reservoir and a graduated glass tube (0-300 mm).
- Armlet or cuff consists of an inflatable linen rubber bag (24 cm × 12 cm) which is fitted with two-pressure rubber tubes. One tube is connected to the mercury reservoir and the other to the air pump.
- The air pump is an oval-shaped thick-walled rubber bulb that fits in the fist used to inflate the armlet. It has a leak valve with an adjustable screw which is used to deflate the armlet.
Principle: Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure exerted by the blood on the walls of the arteries. It is generated by contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of ventricles. Normally, the blood flow through the arteries is streamlined which does not give any sound if the stethoscope is placed on the artery. When the cuff pressure is raised above the expected systolic pressure, the artery becomes completely occluded. When pressure is gradually lowered, the blood starts flowing in the constricted artery producing sounds up to a certain pressure range due to turbulence known as Korotkoff sounds. These sounds are produced in four phases.
| Phase | Fall in pressure | Description of sound |
| I | 10-12 mm Hg | Clear sharp tapping sound due to rushing of blood through the constricted artery. |
| II | 10-15 mm Hg | Murmurish sound |
| III | 12-14 mm Hg | Clear knocking sound |
| IV | 4-5 mm Hg | Muffled and faint and disappears as the blood flow becomes steamline. |
Clinically, the measurement of blood pressure is chiefly used to diagnose various cardiovascular abnormalities.
Procedure for Recording of Blood Pressure:
- Ask the subject to sit or lie down and allow 5 minutes to relax.
- Place the arm of the subject in a position so that it is at the level of the heart.
- Uncover the arm up to the shoulder and tie the cuff around the arm, neither too tight nor too loose.
- Record the blood pressure first with the palpatory method followed by the auscultatory method:
Palpatory method:
- Palpate the radial artery at the wrist and feel the pulse.
- Tighten the screw of the leak valve and inflate the cuff slowly with an air pump until the pulse disappears and note the reading.
Auscultatory method:
- Place the chest piece of the stethoscope on the bifurcation of the brachial artery at the elbow level.
- Inflate the cuff rapidly and raise the pressure 30-40 mm Hg above the reading determined by the palpatory method i.e. reading obtained in step 5.
- Release the pressure gradually using a knob until a clear sharp tapping sound is heard; note this pressure as systolic pressure.
- Continue to release the pressure until the sound disappears; note this pressure as diastolic pressure.
- Take three readings at an interval of 30 minutes with the auscultatory method and find out the average and express the result as systolic/diastolic BP.
Note: Normal BP value is:
- Systolic BP-120 mm Hg.
- Diastolic BP-80 mm Hg
Observation:
- Name:
- Age:
- Gender:
- Date of recording:
- Time of recording:
Observation Table:
| Sr. No. | Systolic BP | Diastolic BP |
| 1. | ||
| 2. | ||
| 3. | ||
| Average B.P |
Result: The blood pressure of the selected subject was found to be …… mm Hg.
Clinical Significance:
| Blood pressure | Indications/Factors responsible |
| Increased | • Obesity, Ageing, Emotional stress, Exercise • Hypertension • Atherosclerosis • Heart diseases • Renal diseases • Diabetes mellitus |
| Decreased | • Hypotension • Severe blood loss • Severe water and electrolyte imbalance |
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Determination of Pulse Rate