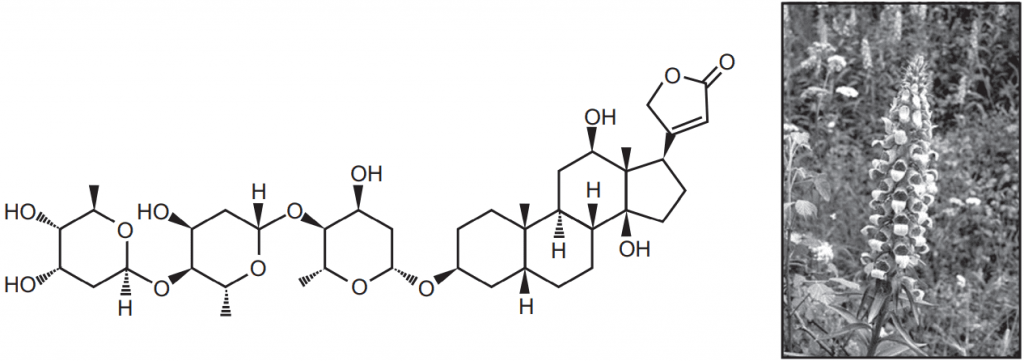
Digoxin is one of the important cardiotonic glycosides obtained from the leaf of Digitalis lanata (Family- Scrophulariaceae). It produces three molecules of digitoxose sugar and one molecule of digoxygenin during hydrolysis. Digoxin hydrolyzed at acidic pH but stable at pH 7. It starts its action within 30 minutes to 2 hours, the half-life is 30-40 hours and major eliminated by the kidney. The melting point of the digoxin is 230-265°C.
Production
Table of Contents
- The dried powdered leaf was extracted with petroleum ether under reduced pressure. Discard the extract and digested the marc with water at 0-4°C so that the polysaccharide may remove. Again the filtrate is discarded and the marc is extracted with alcohol and water.
- Under reduced pressure alcoholic extract is concentrated at 50°C. This concentrate solution is treated with lead acetate to remove the impurities. In the water-soluble glycoside portion (obtain after the treatment of lead acetate) maintain the pH around 6 and then wash with a non-polar solvent.
- Discard the organic layer and treat the aqueous layer with 0.5 percent sodium sulphate to remove the lead sulphate. The aqueous layer is then treated with chloroform and afterwards with ethanol.
- The chloroform portion contains less polar glycoside while the ethanolic portion contains more polar glycoside. The ethanolic portion was further treated and subjected to chromatography to separate the digoxin.
Estimation
Dissolve digoxin (equivalent to 500 mg) in 5 ml solvent (mixture of chloroform: methanol 65:35) and add 20 ml of glacial acetic acid. Shake one hour continuously and filter the solution. Dilute 5 ml of this filtrate to 25 ml with glacial acetic acid which contains 0.005 percent W/V ferric chloride and 2 percent V/V sulphuric acid and allow it to stand for 90 minutes. Measure the absorbance at 519 mµ and compare it with this standard solution prepared in the same way.
TLC study
- Stationary phase: Silica gel G.
- Mobile phase – Cyclohexane: Acetone: Acetic acid (49:49:2).
- Detecting reagent: 5 percent sulphuric acid.
View under UV far light digoxin appears as blue colour, compare with standard
Utilization
Digoxin is an important glycoside from the plant of Digitalis lanata. It increases the myocardial contractility which empties the ventricles. The beginning dose of digoxin is 1 to 1.5 ml but due to its great accumulation tendency, the maintenance dose maintains to 0.25 mg. Comparative to digitoxin, digoxin is short-acting and rapidly eliminated. The use and precaution of the digoxin are the same as digitalis.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Podophyllotoxin
