Isolation of Artemisinin: Artemisinin is isolated from the leaves or aerial part of the plant Artemisia annua (Family-Compositae). It is a sesquiterpene lactone with prominent antimalarial activity with melting point 156-157°C. Artemisinin and its derivatives (Artemether and artesunate) can treat both chloroquine-resistant and chloroquine-sensitive Plasmodium falciparum. The plant is grown in US, Vietnam, and China. It is not native of India but grows successfully in Kashmir. The yellow flower of the plant contains 2-4 times more artemisinin concentration than the leaf. Cultivated varieties have 1.0 percent artemisinin content while wild varieties have 0.01 to 0.5 percent.
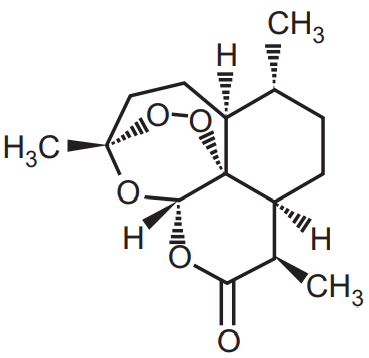
Aerial parts of the plant are extracted with petroleum ether (Boiling point 40-60°C) and concentrated the petroleum ether under vacuum. The concentrated extract is redissolved in chloroform and acetonitrile is added to separate inert plant components like waxes and sugars. Column chromatography of this concentrated extract was performed using silica gel as stationary phase. High artemisinin content fraction will crystallize rapidly. Then recrystallized this fraction using cyclohexane or 50 percent ethanol. Artemisinin is less water-soluble, colourless or white, a crystalline compound having a molecular weight of 282.3 with odourless crystalline powder.
Melting point: 156-157°C.
Thin-layer chromatography of Artemisinin
Dissolve the standard and sample both in chloroform and perform the TLC using mobile phase petroleum ether: Ethyl acetate (1:2). Dry the plate and spray with either ρ-di methylamino benzaldehyde (densitometric scan at 600 nm) or 2 percent solution of vanillin sulphuric acid (densitometric scan 560 nm). Compare the spot of standard and sample. Sesquiterpene can also be estimated by HPLC with UV detection (220 nm). Sesquiterpene can or cannot be converted into their derivative which can absorb UV radiation. In an alkaline medium open the oxygen-containing heterocycles are then converted into lactol in an acidic medium. It can be also estimated using the GC-MS technique by estimating the degradation product (artemisinin is thermal degradable).
Identification Test of Artemisinin
1. 1 gm finely powdered drug is boiled with 10 ml alcohol and filtered. Then add sodium hydroxide to the filtrate and heat again. The red colour develops in liquid.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Isolation of Menthol
