Isolation of Podophyllotoxin: Podophyllotoxin consists of dried roots and rhizomes of Podophyllum emodi or Podophyllum hexandrum belongs to the family Berberidaceae or Podophyllaceae. The content of the resin in the podophyllum depends upon the season of collection, area, part of the plant (i.e root or rhizome.). The roots contain more resin than rhizomes. Podophyllin (resin) extracted from the podophyllum not only contains the podophyllotoxin and dimethyl podophyllotoxin it also contains the podophyllotoxin-1-ο-βD gluco pyranoside, quercitine, kaempferol, and tannins.
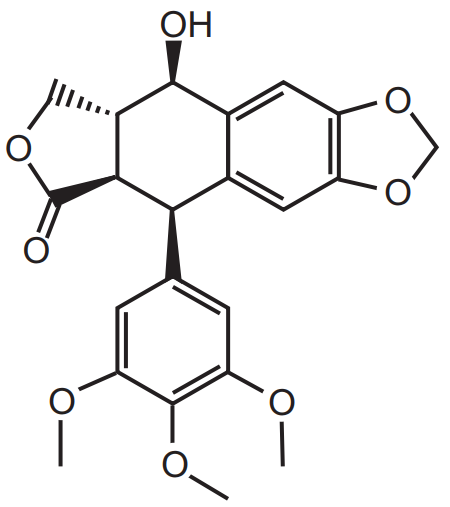
Podophyllotoxin
Root and rhizome of podophyllum emodi is the commercial source of podophyllotoxin. Powder the root and rhizome and extract with methanol or ethanol and concentrate the extract under vacuum. Treat the semisolid mass with acidulated water (10 ml HCl in 1000 ml water) and cool to 10°C slowly. Decanted the settled precipitate and wash it with cold water. On drying this precipitate we get amorphous dark brown powder known as podophyllin.
Extract podophyllin with chloroform and purify by recrystallization with benzene or benzene and ethyl alcohol mixture and then wash with hexane/ petroleum ether which gives the commercial podophyllotoxin.
Thin-layer chromatography of Podophyllotoxin
Dissolve podophyllotoxin in methanol and spot the solution on Silica gel G TLC plates. Elute the TLC plates in a solvent system containing toluene: ethyl acetate (5:7). Sulphuric acid should be used as a detecting reagent. Compare with a standard by scanning 280nm densitometric scan. Violet colour spot will be seen with approx Rf value 0.39.
Identification Test of Podophyllotoxin
- Podophyllotoxin shows violet-blue colour when treated with 50 percent sulphuric acid solution.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Isolation of Glycyrrhetinic Acid
