Aim:
Isolation of microorganisms by streak plate technique.
Requirements:
Peptone, beef/yeast extract, NaCl, agar, alcohol, Petri plate, conical flask, beaker, test tube, nichrome wire loop, glass marking pencil, etc.
Principle:
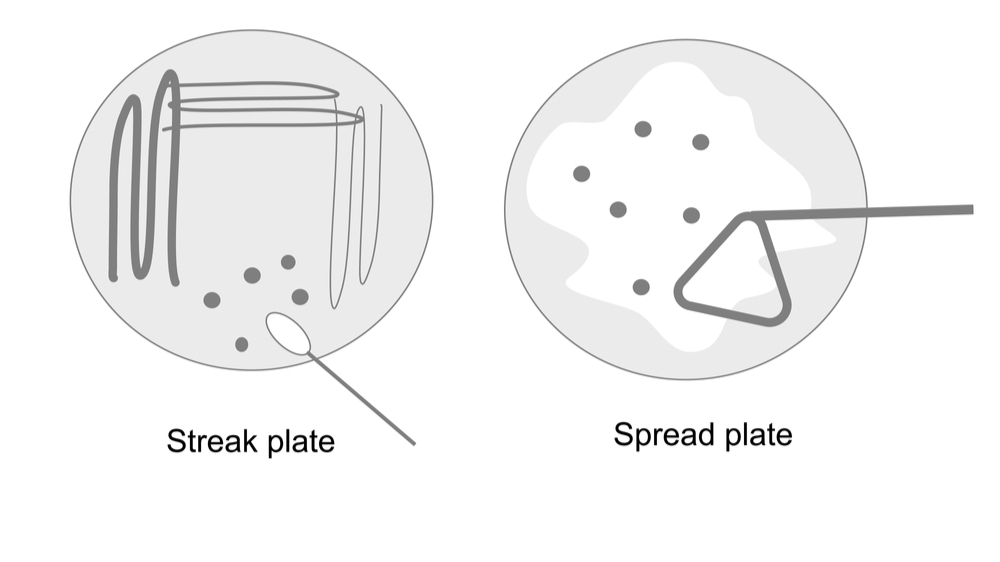
Different techniques used for the purification of cultures are the streak plate method, pour plate method, spread plate method, and micromanipulator. Inoculation of microbial culture to the surface of the sterile agar plate and spreading it by an inoculating wire loop is called the streak plate method. The streak plate technique is used for the cultivation, isolation, and separation of microorganisms from mixed populations. The streak plate technique is used to produce well-separated colonies of bacteria from mixed suspension and the size, shape, colour, and other physical characteristics of isolated colonies are studied.
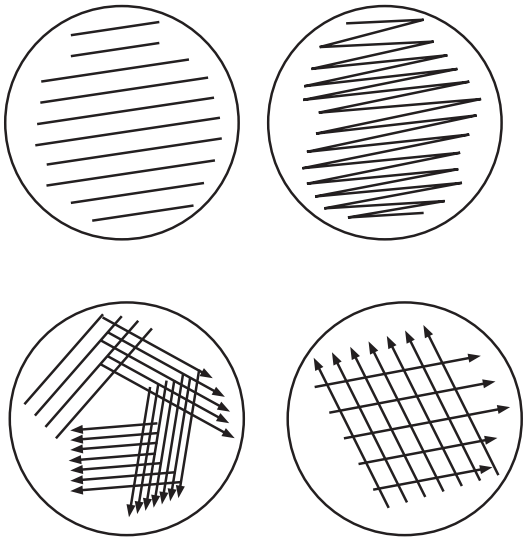
One streak plate, two streak plates four streak plates, and multiple streak plates (Fig.1) are commonly used techniques for the isolation of cultures.
Procedure:
Prepare nutrient agar and sterilize by autoclave at 121°C, 15 lbs for 15 minutes. Pour the medium (about 15 to 20 ml) into Petri plates carefully. Rotate the Petri plate to allow for uniform distribution medium and solidify it. Follow all aseptic conditions to avoid contamination.
Take a small amount of bacterial innoculum by nichrome wire loop from agar slants or agar plates. Carefully lift the lid and streak the culture on the agar medium as shown in Fig.2.
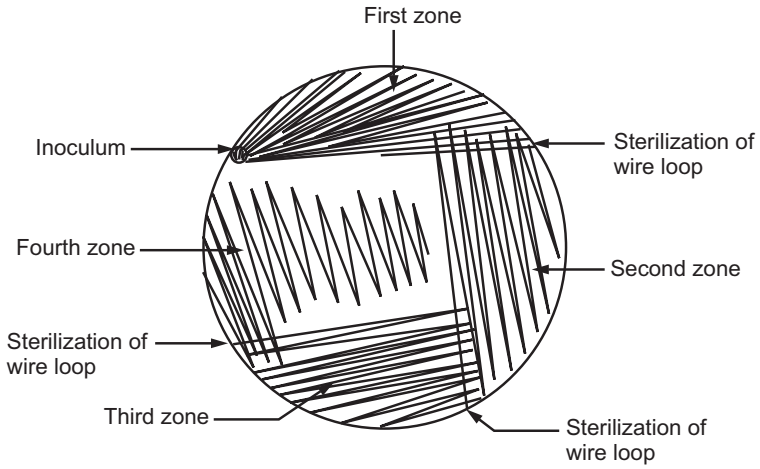
Streak the culture as the first zone by using inoculum and then flame the wire loop to destroy the culture present on the wire loop. By using the first zone, prepare a second zone of inoculum and again flame the wire loop. Prepare the third zone of inoculum by using the second zone and again flame the wire loop. Spread the culture in the fourth zone by using the third zone and finally sterilize the wire loop. Different techniques of streaking may be performed on different Petri plates using the same inoculum. Incubate the Petri plates at 30 to 37°C for 24 to 48 hours.
Observations and Results:
The effect of different techniques of streaking on the growth and separation of colonies may be observed. It is observed that well-developed and isolated colonies have developed at the fourth zone of streaks (Fig.3). Selected isolated colonies that differ in appearance are described as form (circular, irregular), elevation (flat, raised), pigmentation, and size (pinpoint, small, large).

Note:
- After every zone of streaking, the wire loop is sterilized by using a flame and allowed to cool for 10 to 15 seconds before the next streaks (confirmed by touching the agar surface).
- Colonies that are separated (in the fourth zone) may be transferred to agar slants or Petri plates to grow as pure cultures.
- The Petri plate lid should never be lifted completely.
- Do not mix the fourth zone with the first zone at the time of streaking.
- Take less amount of inoculum for isolation of cultures.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Applications Of Cell Cultures