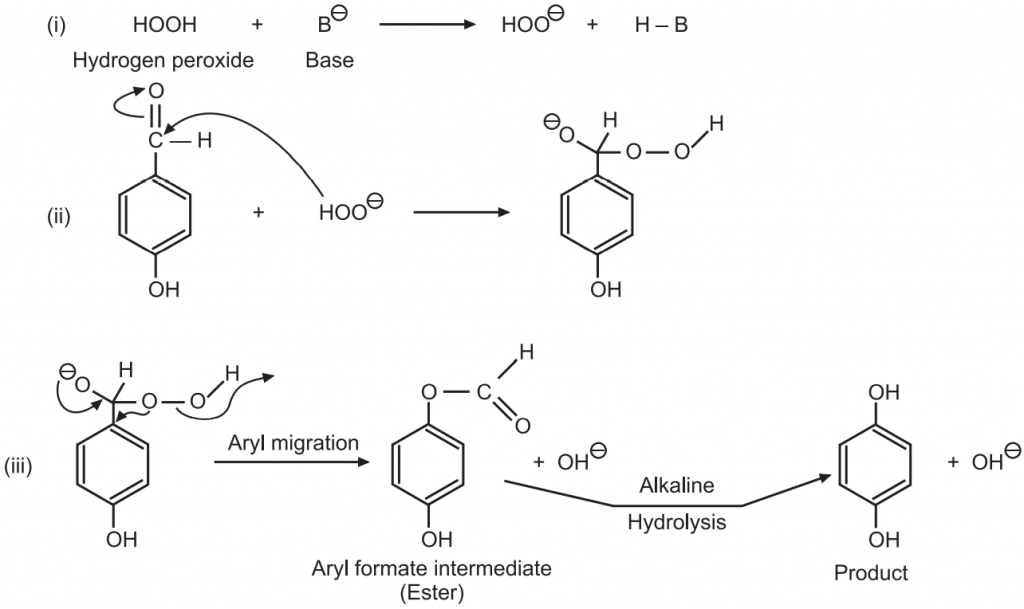
Reaction Mechanism of Dakin Reaction: Dakin Reaction is a redox reaction. An ortho or para-hydroxylated benzaldehyde or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate ion in alkaline conditions.
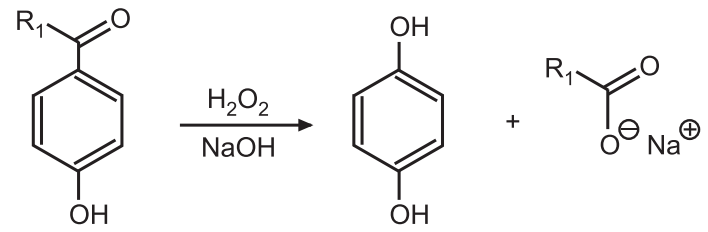
In short, the oxidation of aldehydes or ketones to the corresponding phenol is known as the Dakin reaction.
Reaction Mechanism of Dakin Reaction:
Applications of Dakin reaction:
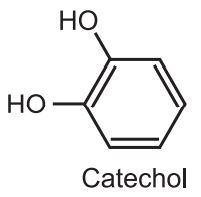
(i) Dakin reaction is used to synthesize catechol. Catechol is used as the starting material for the synthesis of several catecholamines, catecholamine derivatives, and 1, 4- tertbutyl catechol, a common antioxidant, and polymerization inhibitor.
(ii) Dakin’s solution is a dilute hypochlorite solution. Chlorine, the active ingredient in Dakin’s solution, is a strong antiseptic that kills most forms of bacteria and viruses that may lead to skin and tissue infections.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Clemmensen Reduction
