Prescribed Medication Order and Communication Skills: Prescribed medication order is the written directions which are the primary means by which prescribers communicate with pharmacists regarding the specific treatment regimen for a patient. The prescribers may also give medication orders verbally or non-verbally to a registered/licensed pharmacist or nurse. While the medications are sold only on clear, complete, and signed prescription orders.
Medication orders are needed to must have the following points:
- Patient name.
- Name of medication.
- Strength of medication.
- Dose.
- Dosage form.
- Time or frequency of administration.
- Route of administration.
- Quantity to dispense.
- Prescriber name and signature.
- Refill authorization.
- Date.
- PRN medication orders should specify the frequency of administration, maximum daily dosage, and condition for which the medication is being administered.
Interpretation of Prescriptions
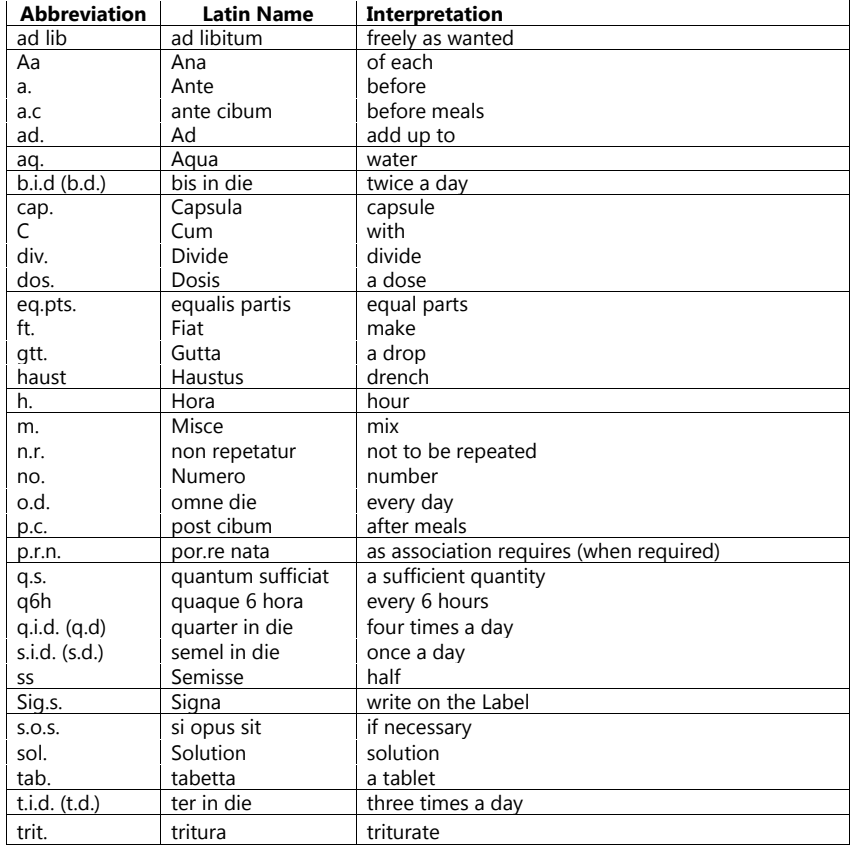
Drug use is a complex process and there are many drugs related challenges at various levels involving prescribers, pharmacists, and patients. While medications misadventure can occur anywhere in the health care system from prescribers to the dispenser to administration and finally to patient use. While many errors can be preventable and pharmacists play important role in the appropriate dispensing of prescribed medications. By interpreting the proper abbreviation involved in the prescription one can effectively interpret the prescription and avoid errors. The following table mentioned the interpretation of commonly used abbreviations and Latin terms while prescribing.
Table.1: Abbreviation and their Interpretation
Legal Requirements
A Prn protocol is required for PRN medication orders which are ordered on a daily/regular basis. So, such medication orders should specify the frequency of administration, maximum daily dosage, and the condition for which medication is being administered. The PRN protocol provides additional information regarding the medication order and to understand the pharmacist when and how much of the prescribed medication to give.
The PRN protocol should include the following points:
- All of the information is found in the regular medication order, along with the following points.
- The specific signs and symptoms for which the medication should be given to a patient.
- A maximum daily dosage.
- Any special instructions, for example, when to call prescribing practitioner or nurse.
Communication Skills
Communication skills are the capability to use language in precise and express information in an easy way to understand with patients and family members, other physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and other health care providers. Effective communication skills are a critical element for patients, pharmacists, and doctors. Communication skills may be verbal or non-verbal way. Following are the three main goals of communication:
- Creating good interpersonal relationships.
- Facilitating the exchange of information.
- Including patients in decision making.
Poor communication skills between pharmacist and patient may lead to the following:
- Inaccurate patient medication history.
- Inappropriate therapeutic decisions.
- Leads to patient confusion, patient disinterest, and patient non-compliance.
Communicating with Health Professionals:
Effective communication between pharmacist and physicians, nurses, and other pharmacists are essential. Following are some instructions and advantages of effective and clear communications between different health professionals involved in patient care services:
- Good doctor-patient communication has the potential to help in regulating patient’s emotions, facilitate comprehension of medical information, and allow for better identification of patient’s needs perceptions, and expectations.
- Patient’s report good communication is more likely to be satisfied with their health care, and especially relevant information for accurate diagnosis of their problems, follow the advice and adhere to the prescribed treatment.
- A more patient-centered communication may provide satisfactory results from the patient as well as from the doctor.
- A pharmacist must notify within a reasonable time after renewing the prescription.
- Pharmacists are periodically required to contact prescribers to manage drug interaction or suggest changes to therapy that could ensure the best possible patient outcomes.
- Manage the drug-related problem by providing your therapeutic recommendation to the prescriber including how to manage this situation.
- Always endeavor to include a reference to the evidence that supports your recommendations this can increase the prescribers comfort level with this and future recommendations.
- Effective written communication to prescribers is essential to provide appropriate and comprehensive patient care.
- Reducing the risks associated with unclear messaging promotes patient safety and quality care.
Communication between Prescribers and Patients:
Effective patient counseling can assist patients in using their medicines safely and reliably. Before giving information, check the patient’s level of understanding. Advice the patient to adapt the medication regimen to their life style. Following are some types of communication required for collecting the information and instructing with patients by health practitioners.
1. Medication History Interviews are required for making decisions. The following information is recorded while communicating with patients:
- Currently or recently prescribed medicines.
- OTC medicines purchased.
- Vaccinations.
- Alternative or traditional remedies.
- Description of reactions and allergies to medicines.
- Medicines were found to be ineffective.
2. Patient Information Leaflet (PILs): Practitioners should use the following outline key information to help/assist the patients and their caregivers/family members in the effective, clear, and safe uses of medicines. The following information should be included while prescribing the medication as well as to be instructed verbally in easy language which can understand the patient, their family members as well as pharmacist and nurses:
- Trade and a generic name.
- Indications for which the medicines are being taken.
- Dosage administrative advice and instructions.
- Information on the action required if a dose is missed.
- Common or serious side effects may occur due to drug administration.
- Storage condition for prescribed medications information.
- Action to be taken if a side effect is an experience.
- Name and contact details of the hospital/physician or health care provider should be provided.
- Author and date of publication of the information.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Pharmacy and Therapeutic Committee
