Synthesis and Medicinal Use of Purine: Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic compound that consists of a pyrimidine ring fused to an imidazole ring. Together with certain pyrimidine bases, purines are constituents of DNA and RNA. Purines also act as hormones and neurotransmitters and are present in some coenzymes.
Biologically important purines include.
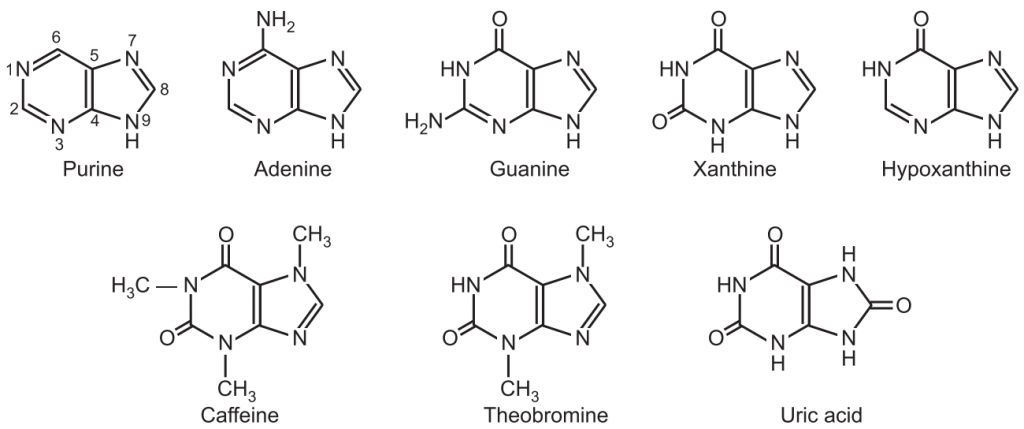
It was first synthesized by German chemist Emil Fischer in 1884.
Synthesis of Purine:
(1)
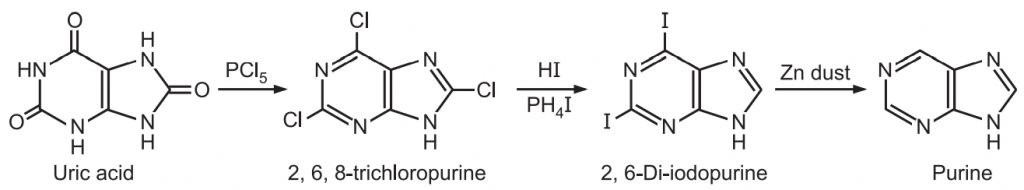
(2) Traube Synthesis:
It begins with a 4-amino-6-hydroxy pyrimidine or 4, 5-diamino pyrimidine involving the nitrosation at 5-position, reduction of nitroso to the amino group using ammonium sulfide, and ring closure with formic acid or chloro carbonic ester.
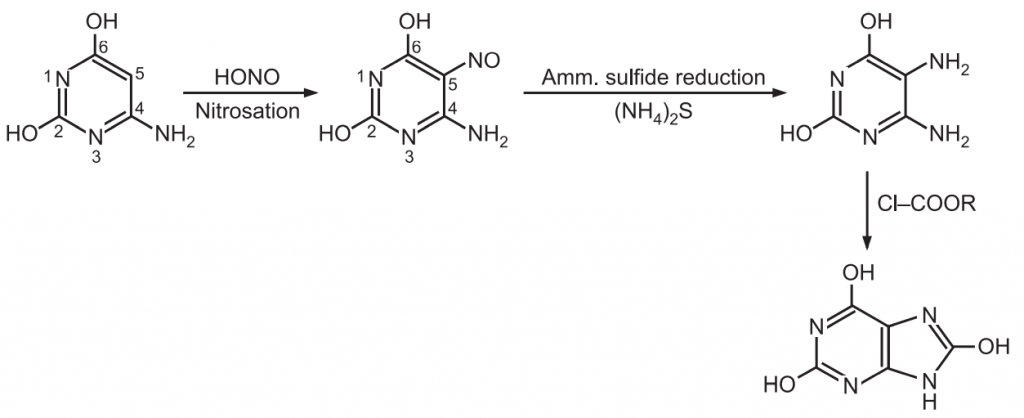
Caffeine synthesis:
Medicinal Uses of Purine:
Purine analogs are having antibacterial, antifungal, antitumor, antiviral, and anti-HIV activity. Important drugs from the purine category include caffeine (CNS stimulant), 6-mercaptopurine (anti-cancer), azithromycin. Drugs having isostere of purine include sildenafil (erectile dysfunction), allopurinol (anti-gout), tubercidin (anti-cancer).
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Synthesis and Reactions of Acridine
